Welcome to our article on the fascinating habitat of African penguins in South Africa.
These unique creatures have captured our imaginations with their charming appearance and captivating behaviors. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of their habitat, exploring where they can be found and the conditions they prefer for breeding and nesting.
Key Takeaways:
- African penguins are native to coastal areas of southern Africa.
- They can be found along the coast, from Namibia to Algoa Bay in South Africa.
- They inhabit both islands and mainland areas, with large breeding colonies on islands and two mainland populations in Betty’s Bay and Boulders Beach.
- African penguins prefer habitats that are flat and sandy with sparse or abundant vegetation, or steep and rocky with sparse vegetation.
- Their nesting sites provide protection and shelter for breeding.
The Physical Characteristics of African Penguins

African penguins, also known as jackass penguins, are fascinating creatures with unique physical adaptations that help them thrive in their natural environment.
These flightless birds have a streamlined body and modified wings that resemble flippers, allowing them to navigate through the water with remarkable speed and agility.
With a thick coat of overlapping feathers, African penguins are well-equipped for life at sea.
These feathers serve multiple purposes, providing waterproofing to keep them dry, wind resistance to help them swim efficiently, and insulation to regulate their body temperature in the cool waters off the southern African coast.
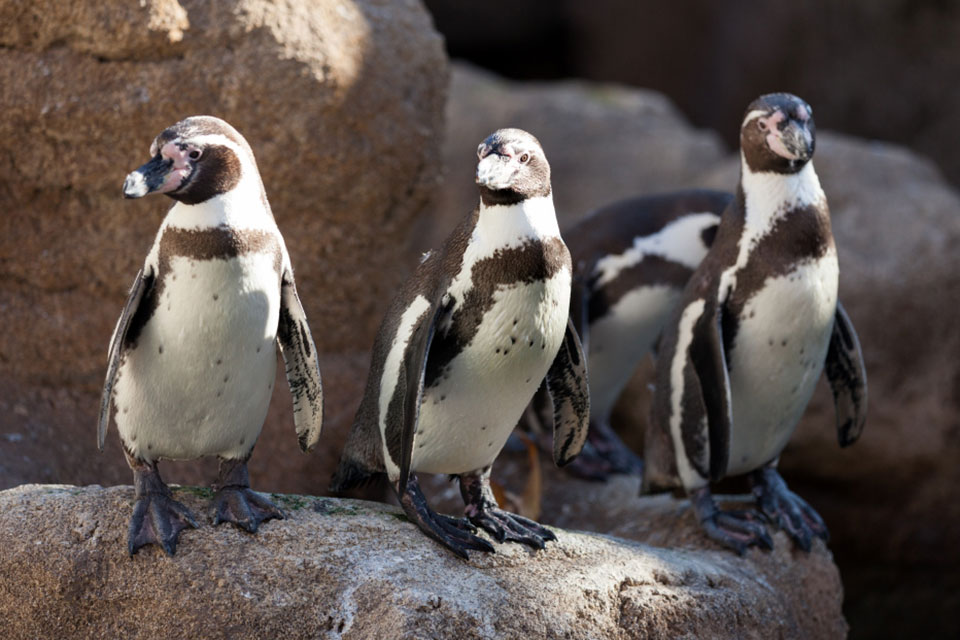
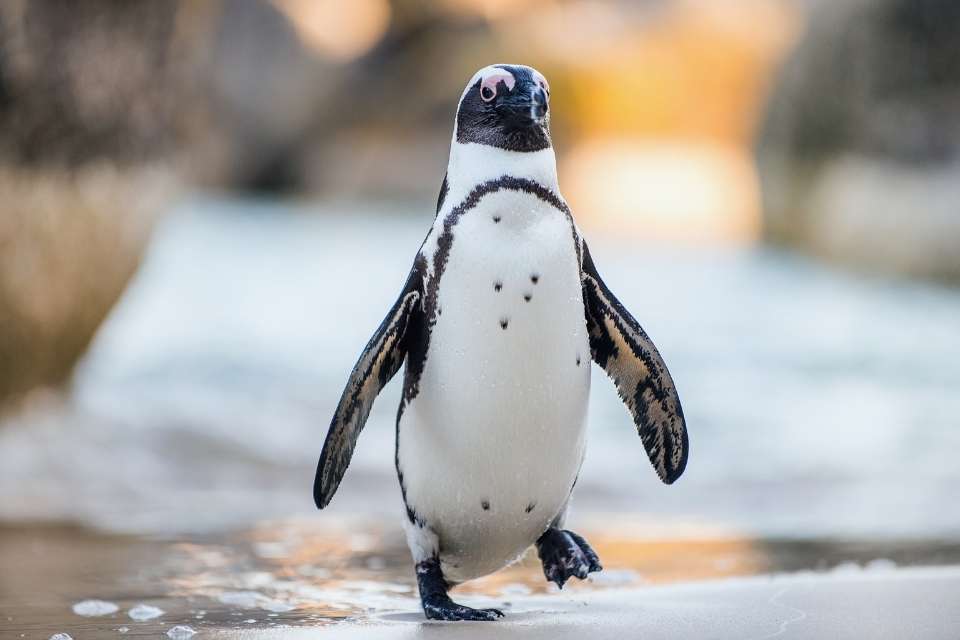
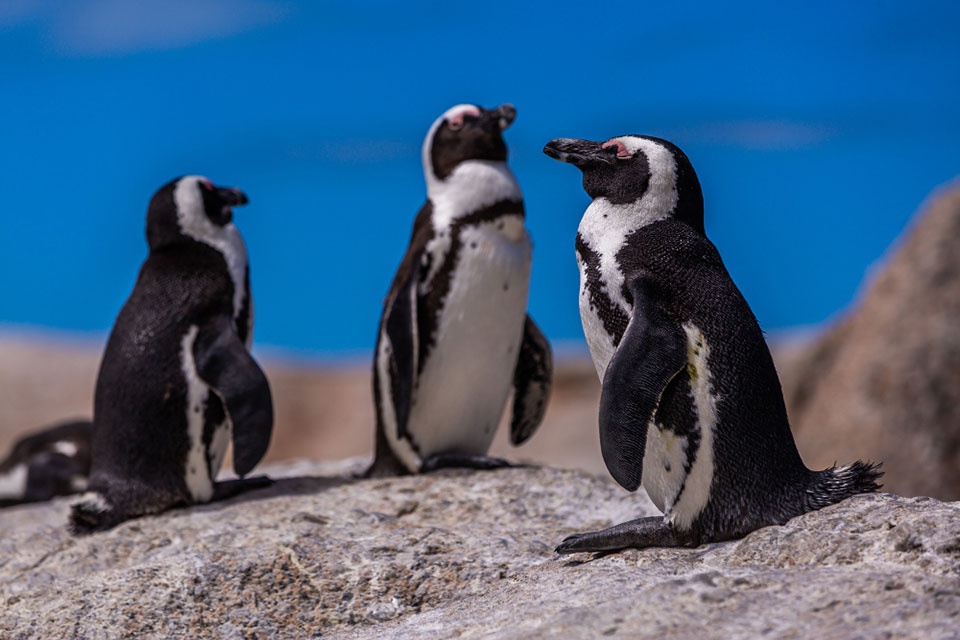
The distinctive appearance of African penguins includes a black back and a white belly, with a thick black stripe across their chest. They have black webbed feet and a black facial mask, which is accentuated by distinctive pink patches of skin above their eyes.
Each penguin has a unique pattern of black spots on their white chest, making them easily identifiable to researchers and conservationists.
“African penguins are not only beautiful creatures, but they also play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of their marine ecosystem.”
Navigating the Challenges of Population Decline
Unfortunately, the African penguin population has experienced significant declines over the past century, primarily due to various human activities.
These penguins are now classified as Endangered, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts to protect their natural habitat and restore their populations.
By understanding the physical characteristics of African penguins and the challenges they face in their natural environment, we can work towards effective conservation strategies.
Together, we can strive to ensure the continued survival of these incredible birds and the preservation of their unique coastal ecosystem.
Habitat and Distribution of African Penguins
African penguins are primarily found along the coastal areas of southern Africa, from Namibia to Algoa Bay in South Africa. They have a preference for specific habitats that offer suitable breeding and foraging conditions.
These habitats can range from flat and sandy areas with sparse or abundant vegetation to steep and rocky terrain with sparse vegetation. It is within these diverse habitats that African penguins form large breeding colonies, which are mainly located on islands.
However, there are also two notable mainland populations of African penguins in Betty’s Bay and Boulders Beach, both in the Cape Town area of South Africa. These mainland colonies provide additional nesting sites for the penguins.
When choosing nesting sites, African penguins prioritize locations that offer protection and shelter for their eggs and chicks. This ensures the survival and well-being of their offspring in their dynamic and challenging ecosystem.
The distribution of African penguins is limited to specific areas along the coast that offer suitable breeding conditions. Their habitat and distribution patterns are closely tied to the availability of food resources and the proximity of suitable nesting sites.
As such, protecting these habitats and preserving their distribution is essential for the long-term survival of African penguins and the diverse marine ecosystems they inhabit.
Feeding Habits and Foraging Behavior
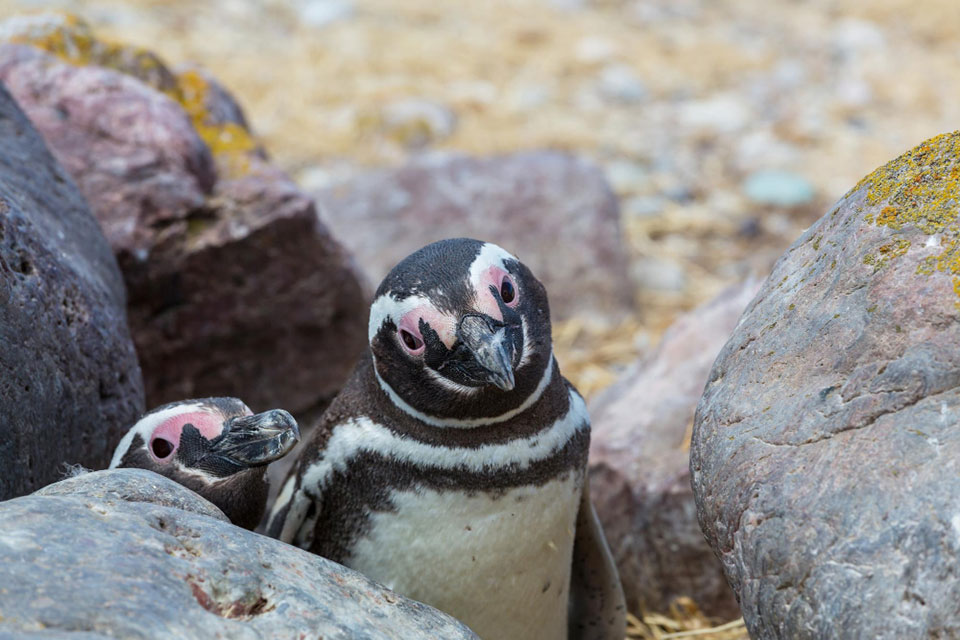

African penguins have unique feeding habits and foraging behaviors that contribute to their survival. These charismatic birds primarily rely on small pelagic fish, such as pilchards, anchovies, horse mackerel, and herring, for their diet.
They may also consume squid and small crustaceans to supplement their food intake. This diverse diet ensures they obtain the necessary nutrients for their growth and overall well-being.
During the breeding season, African penguins tend to forage closer to their colony, typically within a range of 20 to 40 kilometers. This proximity allows them to efficiently gather food for themselves and their chicks.
However, during the non-breeding season, they can travel much further in search of food sources. This adaptability in their foraging behavior enables them to access a wider range of prey, ensuring their survival even in challenging times.
Unfortunately, African penguins face significant challenges in their foraging efforts. Commercial fishing activities have led to a decline in their food resources, resulting in competition for limited prey.
This competition poses a threat to the penguins’ ability to find sufficient food for themselves and their offspring. To address this issue, ongoing research projects are being conducted to evaluate the impact of fishing practices on penguin populations and to develop sustainable fishing guidelines that can help protect their food sources.
Conservation Efforts and Penguin Habitat Restoration
Recognizing the importance of preserving the habitat and food resources of African penguins, various conservation efforts are being undertaken.
These initiatives aim to protect their natural environment, restore breeding colonies, and mitigate the impact of human activities on their populations.
Penguin research projects play a crucial role in gathering essential data and insights into the behavior and needs of African penguins. These projects help us understand their foraging patterns, breeding habits, and response to environmental changes.
The information gathered through these research efforts informs conservation strategies and enables us to make informed decisions to safeguard their future.
In addition to research, habitat restoration is a key focus of conservation efforts.
This involves creating and maintaining suitable nesting sites, ensuring the availability of clean water for the penguins to swim, and protecting their breeding grounds from disturbance. Restoring the natural balance in their habitat is essential for the long-term survival of African penguins.
By joining forces and implementing effective measures, we can make a significant impact on the conservation of African penguins.
Through raising awareness, supporting research projects, and actively participating in habitat restoration initiatives, we can ensure the continued existence of these remarkable birds for generations to come.
Breeding and Life Cycle of African Penguins
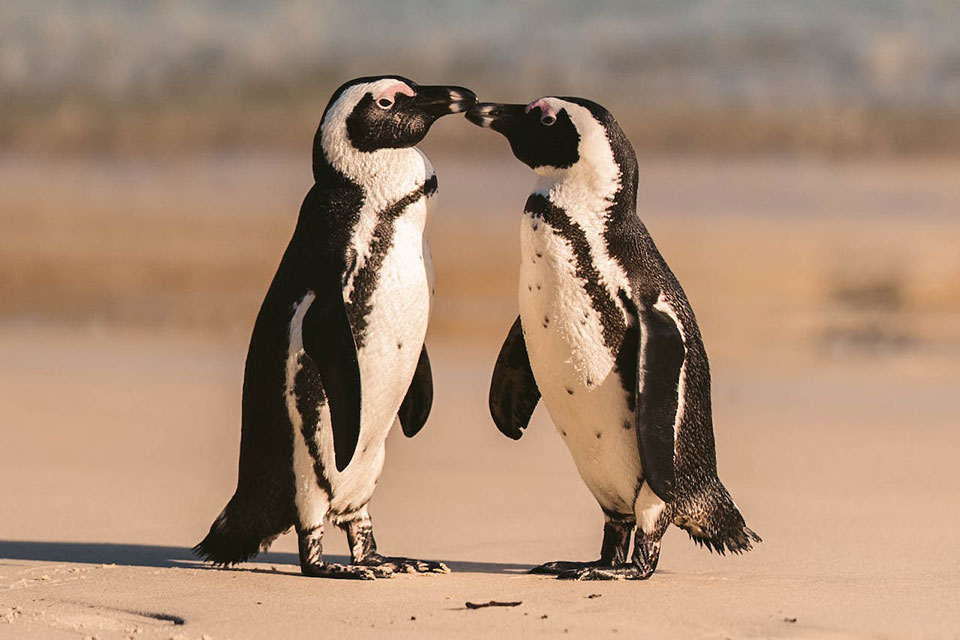

The breeding and life cycle of African penguins is an intricate and fascinating process. These unique birds are monogamous, forming strong pair bonds and returning to the same breeding colonies and nesting sites each year.
Their extended breeding season varies between Namibia and South Africa, with peak periods observed at different times.
During the breeding season, African penguins typically lay one to two eggs per clutch. Both parents take turns incubating the eggs for approximately 38 to 41 days, ensuring their proper development.
The chicks are carefully brooded for the first 15 days before being guarded by both parents for about 30 days. After this period, they join crèches with other chicks, providing them with additional protection.
The chicks become independent after three months and are fully fledged after 70 to 90 days, ready to face the challenges of their environment. It takes four to six years for African penguins to reach reproductive maturity.
Once they have reached this stage, they can continue to breed for many years, contributing to the survival and growth of their species.
Preserving Penguin Habitat and Conservation Efforts
Preserving the habitat of African penguins is crucial for the long-term survival of the species. Efforts are being made to protect their breeding colonies and nesting sites, ensuring the availability of suitable environments for their reproduction and upbringing.
Conservation organizations, researchers, and local communities are working together to mitigate the impact of human activities on penguin populations.
Conservation initiatives include habitat restoration, where suitable nesting areas are created or enhanced to provide additional opportunities for penguins to breed.
These efforts aim to increase the overall number of breeding pairs and improve the chances of successful reproduction. Monitoring and research projects are also in place to gather valuable data on penguin populations, breeding success, and the effectiveness of conservation measures.
Through collaborative actions and a commitment to the preservation of these remarkable birds, we can ensure that African penguins continue to thrive in their natural habitat, contributing to the biodiversity and beauty of the South African coastal regions.
Conservation Status and Threats to African Penguins
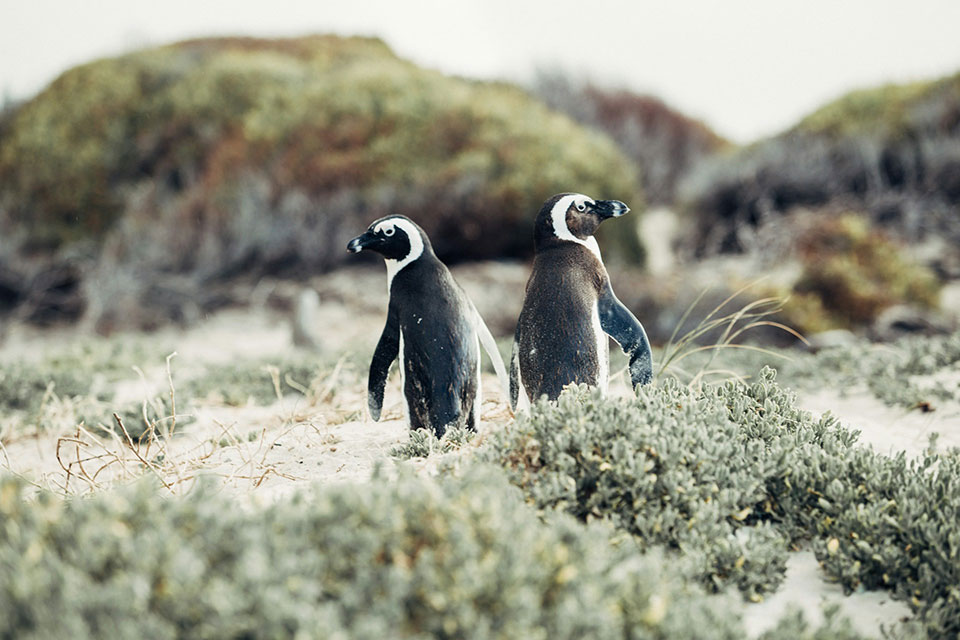

The African penguin population is currently facing significant conservation challenges, and their conservation status is classified as Endangered by the IUCN Red List.
These charismatic penguins have experienced rapid declines due to various threats, including overexploitation for food, habitat modification, oil spillages, and competition for food resources with commercial fishing.
One of the major threats to African penguins is the reduction of guano deposits, which they rely on for nesting. The loss of suitable nesting sites has had a detrimental impact on their breeding success.
Additionally, the destruction of their natural habitat, such as the destruction of coastal vegetation, has further exacerbated their vulnerability.
Conservation efforts are underway to protect and restore African penguin populations. These efforts include the establishment of protected areas, habitat restoration projects, and the mitigation of human activities that negatively impact their habitats.
Ongoing research projects and monitoring programs also play a crucial role in understanding the population dynamics and identifying effective conservation strategies.
By raising awareness about the conservation needs of African penguins and implementing targeted conservation actions, we can work towards ensuring the survival of this iconic species and preserving their natural environment.
Adaptations and Behavior of African Penguins
African penguins have fascinating adaptations that enable them to thrive in their natural environment. Their streamlined bodies and modified wings, resembling flippers, make them excellent swimmers, reaching speeds of up to 20 km/h.
Their black backs blend with the water when viewed from above, providing camouflage, while their white bellies make it hard for predators to spot them underwater.
These penguins also have pink patches of skin above their eyes, which help regulate their body temperature. The blood vessels in these patches expand or contract to release or retain heat, ensuring their comfort in varying weather conditions.
This adaptation is essential in their interaction with the African penguin ecosystem.
African penguins exhibit various social behaviors, including vocalizations, grooming, and preening. They communicate through a range of calls, such as braying, trilling, and honking, each serving a different purpose.
They engage in grooming and preening to maintain their feathers’ condition, ensuring effective waterproofing and insulation. These behaviors play a crucial role in their social dynamics within the penguin community.
Conservation Efforts
To protect African penguins and preserve their natural habitat, several conservation efforts are underway. Habitat restoration projects aim to create suitable breeding and foraging environments by removing invasive species and restoring coastal vegetation.
By rehabilitating nesting sites and improving guano deposits, conservationists encourage penguin populations’ growth and sustainability.
Research projects play a vital role in understanding the African penguin ecosystem and identifying effective conservation strategies. Scientists study breeding patterns, foraging behavior, and population dynamics to inform management plans.
They work closely with local communities and fishing industries to implement measures that minimize the impact on penguin populations, such as regulating fishing practices and reducing pollution levels.
Predators and Conservation Efforts
African penguins face threats from a variety of predators, both at sea and on land. Cape fur seals, sharks, killer whales, mongoose, Cape genet, domestic cats, and leopards are among their predators.
These predators pose a significant risk to the penguins’ survival, as they prey on both adult penguins and their eggs and chicks. In addition to natural predators, African penguins also face threats from human activities such as fishing and pollution.
Conservation efforts are being implemented to protect and restore African penguin populations.
These efforts include habitat restoration, research projects, and measures to mitigate the impact of human activities on the penguins’ natural environment. By restoring and protecting their breeding colonies and nesting sites, we can provide a safe and suitable habitat for African penguins to thrive.
Research projects play a crucial role in understanding the behavior, ecology, and conservation needs of African penguins. These projects help us gather important data on their population dynamics, foraging patterns, and breeding success.
Through ongoing research, we can identify the key factors affecting their populations and implement targeted conservation strategies to address these challenges.
Overall, African penguin conservation is a collaborative effort that requires the involvement of scientists, conservation organizations, local communities, and government authorities.
By working together, we can ensure the long-term survival of this iconic species and protect their natural environment for future generations.
Conclusion
The African penguin is a remarkable species that captivates us with its unique characteristics. From its streamlined body and modified wings for efficient swimming to its distinctive black and white coloration, these penguins are truly a marvel of nature.
However, the African penguin faces significant conservation challenges. With its population rapidly declining, it is now classified as Endangered. Overexploitation for food, habitat modification, and competition for resources are major threats to their survival.
It is imperative that we take action to protect and conserve these wonderful creatures. By raising awareness about African penguin facts and the importance of their natural environment, we can inspire people to support penguin conservation efforts.
Restoring their habitat, implementing research projects, and mitigating the impact of human activities are essential steps toward ensuring the future of African penguins.
Together, we can make a difference. Let us join hands and work towards preserving these magnificent penguins and their natural environment for generations to come.
FAQ
Where are African penguins found?
African penguins are found along the coastal areas of southern Africa, from Namibia to Algoa Bay in South Africa. They mainly inhabit islands, but there are also two mainland populations in Betty’s Bay and Boulders Beach.
What type of habitat do African penguins prefer?
African penguins prefer habitats that are flat and sandy with sparse or abundant vegetation, or steep and rocky with sparse vegetation.
What do African penguins eat?
African penguins primarily feed on small pelagic fish such as pilchards, anchovies, horse mackerel, and herring. They may also supplement their diet with squid and small crustaceans.
How do African penguins breed and raise their young?
African penguins are monogamous and return to the same breeding colony and nesting site each year. They usually lay one to two eggs per clutch, and both parents take turns incubating the eggs.
The chicks are brooded for the first 15 days and then guarded by both parents. After that, they join crèches with other chicks for protection.
Why are African penguins endangered?
African penguins are classified as Endangered due to overexploitation for food, habitat modification, oil spillages, and competition for food with commercial fishing. The reduction of guano deposits, which the penguins used for nesting, has also posed a threat.
How do African penguins adapt to their environment?
African penguins have several adaptations that allow them to survive in their natural environment.
They are highly efficient swimmers, have a black back which blends with the water, and white bellies which make them difficult to spot by predators under the water. They also have pink patches of skin above their eyes, which help regulate their body temperature.
What are the predators of African penguins?
African penguins face threats from predators both at sea and on land, including Cape fur seals, sharks, killer whales, mongoose, Cape genet, domestic cats, and leopard. Their eggs and chicks are preyed upon by kelp gulls, herons, rats, and African sacred ibises.
What conservation efforts are being made to protect African penguins?
Conservation efforts include habitat restoration, research projects, and measures to mitigate the impact of human activities such as fishing and pollution.