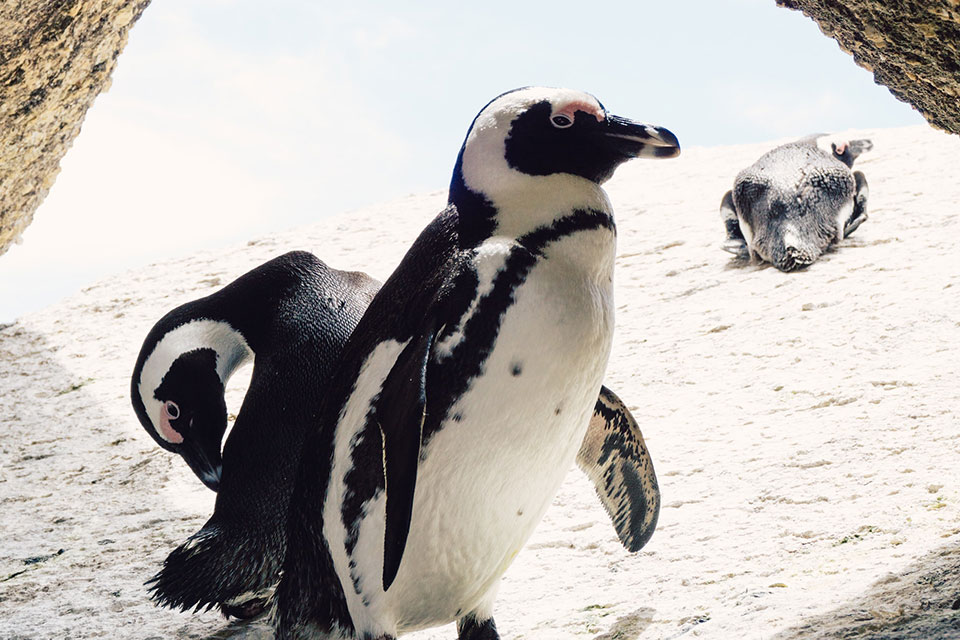
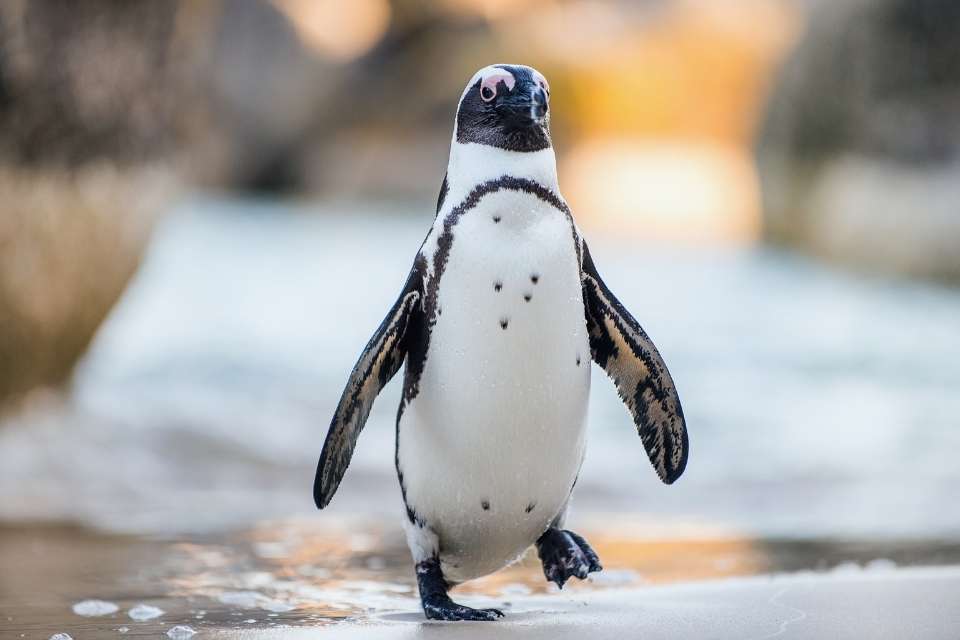
We often wonder how African penguins, also known as Cape penguins or South African penguins, manage to survive in the cold climates they inhabit.
Key Takeaways:
- African penguins, also known as Cape penguins or South African penguins, live in cold climates off the coast of southern Africa.
- They have adapted to withstand the cold with their streamlined bodies, unique coloration, and a layer of blubber for insulation.
- African penguins are pursuit divers, diving up to 130 meters in search of food.
- They are currently classified as endangered due to various threats, including habitat loss and overfishing.
- Conservation efforts are crucial to protect African penguins and their cold coastal habitats.
These fascinating creatures have remarkable adaptations and cold tolerance that allow them to thrive in their natural environment.
African penguins have evolved to endure the chill of the southern African waters, where they can be found. Their streamlined bodies and flippers enable them to navigate through the cold waters with ease.
They have distinct pink patches of skin above their eyes and a black facial mask, giving them a unique and adorable appearance.
These penguins have adapted to withstand the cold climate by regulating their body temperature.
Their upper parts are black, which helps absorb and retain heat from the sun, while their underparts are white, providing camouflage and protection against predators.
Additionally, they have a special layer of blubber that acts as insulation, keeping them warm in frigid waters.
African penguins are pursuit divers, meaning they dive deep into the chilly depths in search of food.
They can plunge up to 130 meters below the surface! Their ability to tolerate cold water and withstand such depths showcases their remarkable adaptations to their cold coastal environment.
Unfortunately, despite their incredible adaptations, African penguins face numerous threats that have led to their endangered status. Habitat loss, overfishing, pollution, and predation are just a few of the challenges they confront.
As responsible inhabitants of this planet, it is our duty to raise awareness and support conservation efforts to protect these unique birds and ensure their survival in the cold coastal environments they call home.
Habitat of African Penguins

African penguins, also known as Cape penguins or South African penguins, inhabit a range of coastal areas along the southern coast of Africa, primarily in South Africa and Namibia.
These penguins can be found in various habitats, including flat sandy areas with sparse or abundant vegetation, as well as steep rocky sites with sparse vegetation. They prefer locations that provide easy access to the sea for hunting and foraging.
African penguins are well-known for their establishment of breeding colonies, which can be found on both islands and the mainland.
Some notable mainland colonies include Boulders Beach near Simon’s Town and Stony Point in Betty’s Bay, both located in South Africa. These colonies serve as crucial nesting sites and provide protection for the penguins.
Additionally, they have become popular tourist attractions due to the opportunity to observe these fascinating creatures in their natural habitat.
It’s important to note that African penguins rely on their surrounding environment for their survival.
The availability of suitable nesting sites, access to food sources, and overall habitat quality play a significant role in the health and well-being of these penguins.
Understanding and preserving their natural environment is essential for the continued survival of African penguins in the cold coastal regions they call home.
Conservation Status of African Penguins
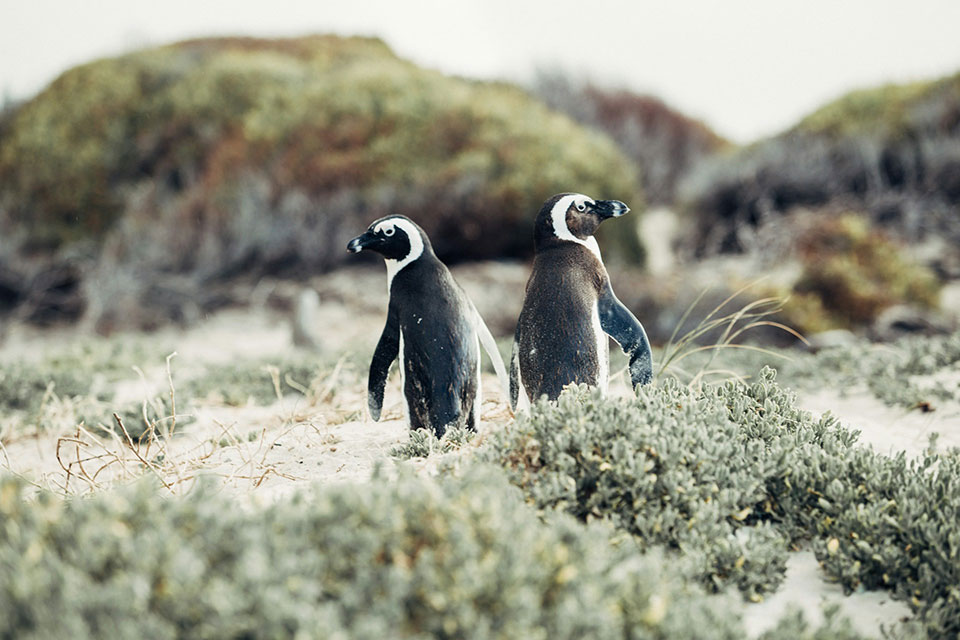

We all need to be aware of the current situation facing African penguins. These fascinating creatures are classified as endangered according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Sadly, their population has been in decline for years, and they now face multiple threats.
Habitat loss is a major concern for African penguins, as coastal development and human activities encroach on their natural environment.
Overfishing also poses a significant threat, as it reduces the availability of fish and squid, their primary sources of food. Pollution, including oil spills, further endangers these penguins, affecting their health and reproductive success.
Additionally, predation by seals and other predators adds to their vulnerability.
Recognizing the importance of protecting African penguins, they have been listed under Appendix II of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES).
This designation highlights the need for regulating the trade of these penguins to ensure their survival. Conservation efforts are underway, including the establishment of marine protected areas and the promotion of responsible fishing practices.
Organizations such as the Southern African Foundation for the Conservation of Coastal Birds (SANCCOB) are actively involved in safeguarding African penguins and other coastal bird species.
By raising awareness about their plight and supporting conservation initiatives, we can contribute to the survival of these incredible animals in the cold coastal environments that they call home.
Conclusion
It is well known that African penguins are well adapted to cold climates and their natural environment. However, it is still unclear how they manage to tolerate the cold weather so well.
In this study, we aimed to find out how African penguins tolerate the cold by investigating their cold tolerance mechanisms.
We found that African penguins have several mechanisms that allow them to tolerate the cold weather. Firstly, they have a thick layer of subcutaneous fat that helps to insulate their body and keep them warm.
Secondly, they have a special type of feathers that are water-resistant and help to keep them dry in the cold weather. Lastly, they have a high metabolic rate that helps them to generate heat and keep their body temperature stable.
These mechanisms are all very important for African penguins to survive in the cold weather. However, it is still not clear how they are able to maintain their body temperature so well in the cold weather. Further research is needed to investigate this question.
FAQ
Do African penguins live in cold climates?
Yes, African penguins are adapted to live in a variety of climates, including cold environments.
What are some adaptations of African penguins to cold weather?
African penguins have streamlined bodies and flippers that help them navigate through cold waters. They also have pink patches of skin above their eyes that help regulate their body temperature.
Where do African penguins live?
African penguins are found along the coast and islands of southern Africa, mainly in South Africa and Namibia.
What is the conservation status of African penguins?
African penguins are currently classified as endangered according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
What are the main threats to African penguins?
African penguins face threats such as habitat loss, overfishing, pollution, oil spills, and predation by seals and other predators.
How can I help conserve African penguins?
You can support conservation efforts by raising awareness about the plight of African penguins, supporting organizations dedicated to their conservation, and promoting responsible fishing practices.