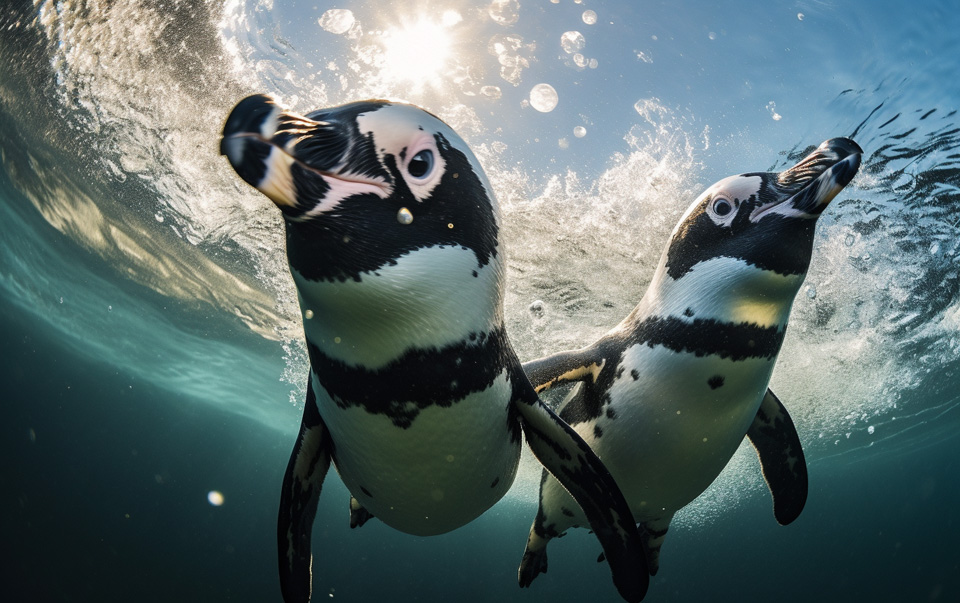
Penguins are remarkable creatures with unique abilities to stay submerged in water for extended periods of time.
Their underwater prowess is a marvel to behold, as they navigate the depths with grace and skill. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of penguin underwater ability, breath-holding capacity, and diving behavior.
Penguins have unique adaptations that allow them to stay underwater for extended periods of time. The Emperor Penguin, in particular, can dive to depths of over 500m and stay submerged for up to 27 minutes.
Key Takeaways:
- Penguins have remarkable adaptations that allow them to stay underwater for extended periods of time.
- The Emperor Penguin can dive to depths of over 500m and stay submerged for up to 27 minutes.
- Penguins slow their heart rate, conserve oxygen, and have specialized haemoglobin to support their extended underwater stay.
- They also have solid bones and the ability to reduce metabolism and shut down non-essential organ functions.
- Penguins have streamlined bodies, paddle-like flippers, and well-developed muscles for efficient swimming.
The Incredible Aquatic Adaptations of Penguins
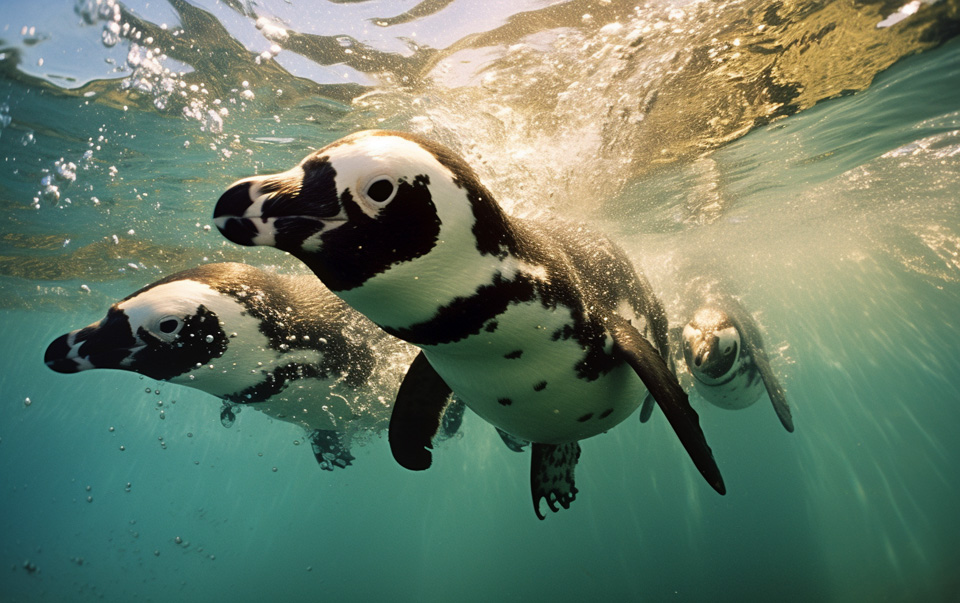

Penguins have a range of adaptations that enable them to thrive in aquatic environments. These incredible adaptations allow them to swim with efficiency and survive underwater for extended periods.
Let’s explore some of the remarkable abilities that make penguins exceptional aquatic creatures.
Streamlined Bodies and Paddle-like Flippers
Penguins have streamlined bodies that minimize drag as they propel themselves through the water. Their paddle-like flippers, located on their wings, act as powerful and efficient propellers.
These adaptations allow penguins to navigate the underwater world with ease and agility.
Solid, Dense Bones
Overcoming buoyancy is crucial for penguins to dive and swim effectively underwater. Penguins have solid and dense bones, which help them stay submerged and maintain their streamlined shape. This adaptation ensures that they can maneuver swiftly and with precision.
Additional Oxygen Storage and Metabolism Regulation
Penguins have muscle tissues that can store additional oxygen, enabling them to endure longer periods without breathing while underwater. This adaptation is vital for their ability to dive to great depths and survive in low-oxygen environments.
Penguins can also regulate their heart rate and reduce their metabolism, conserving energy and maximizing their endurance during dives.
Glands for Salt and Fluid Excretion
Penguins have special glands located under their eyes that help them excrete excess salt and fluid from their bodies. This adaptation allows them to drink seawater without experiencing any adverse effects.
By maintaining the delicate balance of salt and fluid levels, penguins can thrive in their marine habitat.
These incredible aquatic adaptations, combined with their ability to regulate their heart rate, reduce metabolism, and excrete excess salt and fluid, contribute to penguins’ success in the underwater world.
They exemplify nature’s ingenuity and serve as a testament to the remarkable diversity of life on our planet.
Diving and Swimming Behavior of Penguins
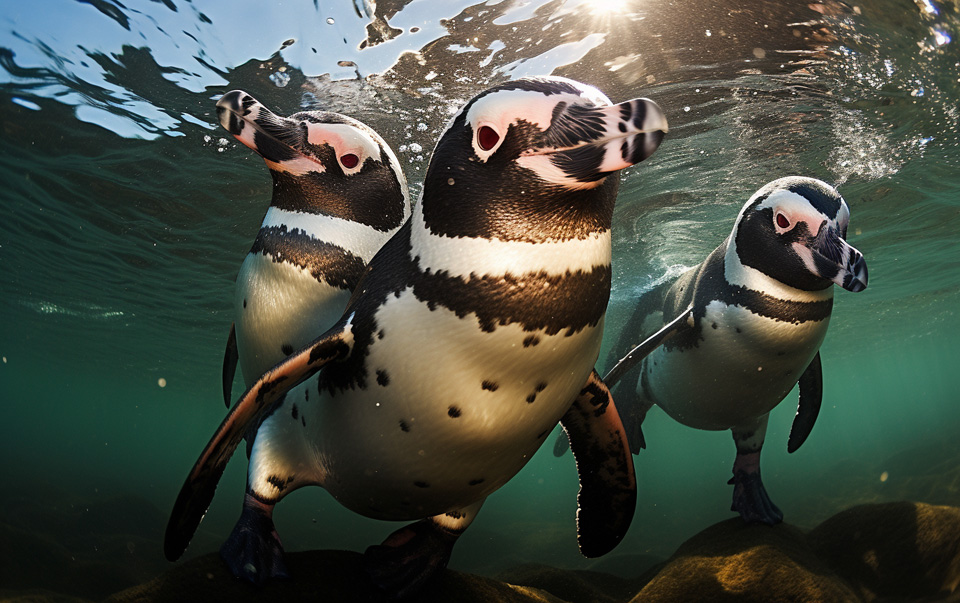

Different species of penguins exhibit fascinating diving behaviors, showcasing their remarkable underwater capabilities. Let’s take a closer look at how these marvelous creatures conquer the depths.
Diving Duration
Penguins are known for their impressive breath-holding abilities. While most species typically stay submerged for less than a minute, their dives can vary in duration from a few seconds to several minutes.
However, there are exceptional species that take diving to extraordinary depths and durations.
One such species is the Emperor Penguin, renowned for its deep dives. Emperor Penguins can descend to staggering depths of up to 565 meters, remaining underwater for a remarkable 27.6 minutes.
This endurance is made possible by their unique adaptations, including the ability to slow their heart rate and conserve oxygen.
Other species, such as the Adélie and King Penguins, have also been observed diving to impressive depths of over 100 meters, underscoring their exceptional diving abilities.
Swimming Speeds
Penguins are not only skilled divers but also adept swimmers, effortlessly gliding through the water with considerable speed. Although swimming speeds vary among different species, they all navigate the depths with admirable agility.
The Emperor Penguin, once again, takes the lead in terms of swimming speed, reaching remarkable speeds of up to 8.9 mph. King Penguins, another species known for their aquatic prowess, can achieve speeds of up to 7.6 mph.
It’s nature’s symphony of grace and power as penguins harness their streamlined bodies, strong flippers, and well-developed muscles to propel themselves through the water.
With their remarkable diving behavior and impressive swimming speeds, penguins are truly the epitome of adaptability in the aquatic world.
From the Emperor Penguin’s deep dives and extended underwater stays to the King Penguin’s agile swimming prowess, these fascinating creatures navigate their watery habitats with finesse and determination.
Swimming and Breathing Techniques of Penguins
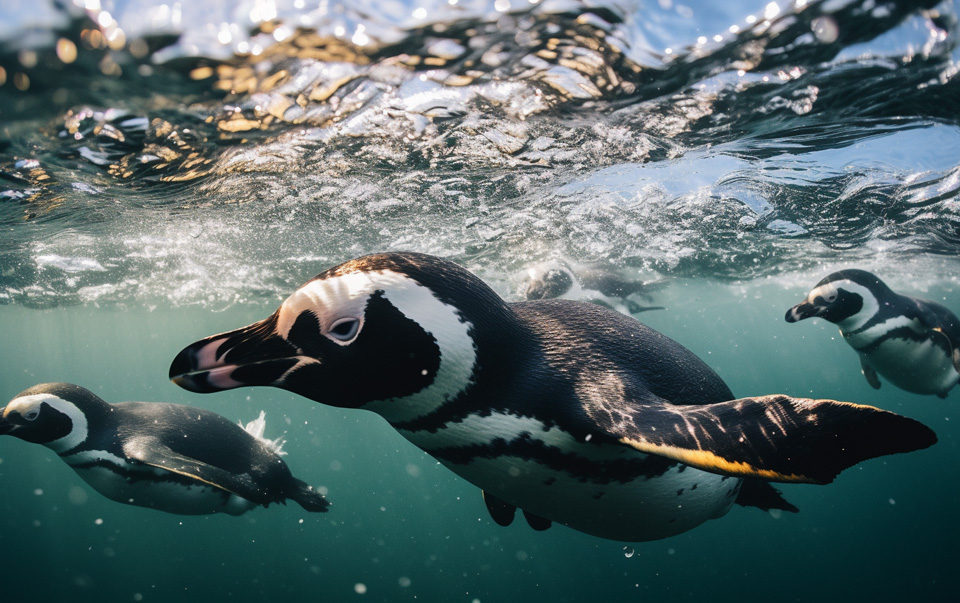

Penguins are known for their remarkable swimming capabilities and unique breathing techniques, especially when near the water’s surface. Different penguin species employ various techniques to navigate through the water and optimize their breathing during these moments.
One such technique is known as porpoising, which is observed in species like the Gentoo Penguin. When porpoising, these penguins rapidly inhale and exhale while leaping in and out of the water.
This technique allows them to maintain a steady speed and continuous forward movement without interruptions.
However, it’s important to note that not all penguin species exhibit porpoising behavior. Penguins, in general, rely on deep inhalation before diving and may slightly inhale just before submerging themselves to increase their oxygen stores.
During their time underwater, penguins have the remarkable ability to regulate their air intake. They can preserve energy during ascents by using the expanding air volume in their bodies, effectively reducing the need to breathe as frequently.
Penguins have developed specific adaptations to excel in swimming and breathing near the water’s surface. These adaptations, combined with their efficient swimming techniques and unique breathing strategies, contribute to their success in their aquatic environment.
Penguin Swimming Speeds
In the vast expanses of the ocean, penguins gracefully glide through the water, showcasing their impressive swimming abilities. These remarkable creatures exhibit different swimming speeds depending on their species, each adapted to thrive in their unique environments.
The largest penguin species, the Emperor Penguin, is known for its impressive swimming speed. It can reach speeds of up to 8.9 mph (14.3 km/h), propelling itself through the water with its well-developed wing and breast muscles.
This speed allows the Emperor Penguin to navigate through its icy Antarctic habitat with agility and efficiency.
Another species, the King Penguin, also demonstrates impressive swimming capabilities. It achieves maximum speeds of around 7.6 mph (12.2 km/h), thanks to its powerful muscles and streamlined body.
The Gentoo and Adélie Penguins, known for their agility and grace in the water, typically swim at speeds ranging from 4.3 to 6.2 mph (6.9 to 10 km/h). These species utilize their wing and breast muscles to propel themselves through the water, using movements that resemble the wingbeats of flying birds.
On the other end of the spectrum, the Little Penguin shows a slower swimming speed, typically reaching speeds of about 1.6 mph (2.6 km/h).
Despite their slower pace, these small penguins navigate their coastal habitats with ease, utilizing their streamlined bodies and dense bones to overcome buoyancy and maintain their shape.
“Penguins are truly remarkable swimmers, showcasing a diverse range of swimming speeds across different species. From the impressive speed of the larger Emperor and King Penguins to the agile movements of the Gentoo and Adélie Penguins, each species has finely tuned its swimming abilities to thrive in its unique environment.”
Penguins, with their varying swimming speeds and incredible adaptations, captivate us with their prowess in the water. They navigate their watery world with grace and efficiency, demonstrating nature’s ingenuity in its diverse forms.
Conclusion
Penguins are truly remarkable creatures with extraordinary underwater abilities. Their unique adaptations allow them to thrive in the aquatic environment and demonstrate their mastery of diving behavior.
Through their ability to slow their heart rate, conserve oxygen, and reduce metabolism, penguins can stay underwater for extended periods.
With their streamlined bodies, paddle-like flippers, and well-developed muscles, penguins exhibit exceptional swimming capabilities. Their efficient swimming techniques, combined with their ability to regulate air intake and utilize specific breathing techniques, optimize their diving performance.
These aquatic adaptations enable penguins to explore the depths of the ocean and withstand the challenges of the underwater world.
From the Emperors diving to great depths of up to 500m, to the Adélie and King Penguins reaching depths of over 100m, penguins truly showcase their underwater abilities.
In conclusion, penguins are a testament to the wonders of nature. Their ability to stay underwater and navigate through the ocean depths is a testament to their remarkable evolutionary qualities.
The combination of their unique adaptations and swimming prowess makes penguins true aquatic marvels.
FAQ
How long can penguins stay underwater?
Penguins have unique adaptations that allow them to stay underwater for extended periods of time. The Emperor Penguin, in particular, can dive to depths of over 500m and stay submerged for up to 27 minutes.
What adaptations do penguins have to survive underwater?
Penguins have streamlined bodies and paddle-like flippers that help them swim efficiently through the water. They also have specialized haemoglobin, solid bones, and the ability to reduce metabolism and shut down non-essential organ functions, all of which contribute to their extended underwater stay.
What is the diving behavior of penguins?
Different species of penguins exhibit varying diving behaviors. Most species stay submerged for less than a minute, with dives ranging from a few seconds to several minutes. The Emperor Penguin is known for its deep dives, reaching depths of up to 565m and staying under for up to 27.6 minutes.
How do penguins swim and breathe near the water’s surface?
Penguins breathe in deeply before diving and may slightly inhale just before a dive to increase their oxygen stores. Some species, such as the Gentoo Penguin, use a technique called porpoising, where they rapidly inhale and exhale while leaping in and out of the water to maintain a steady speed and forward movement.
What are the swimming speeds of penguins?
Penguins have different swimming speeds depending on their species. Emperor Penguins have been observed swimming at speeds up to 8.9 mph, while King Penguins have recorded maximum swim speeds of 7.6 mph. Gentoo and Adélie Penguins typically swim at speeds ranging from 4.3 to 6.2 mph.
How do penguins survive and thrive underwater?
Penguins possess remarkable abilities to stay underwater for extended periods of time. Through their unique adaptations, such as slowing their heart rate, conserving oxygen, and reducing metabolism, they can dive to great depths and withstand the challenges of the underwater environment.