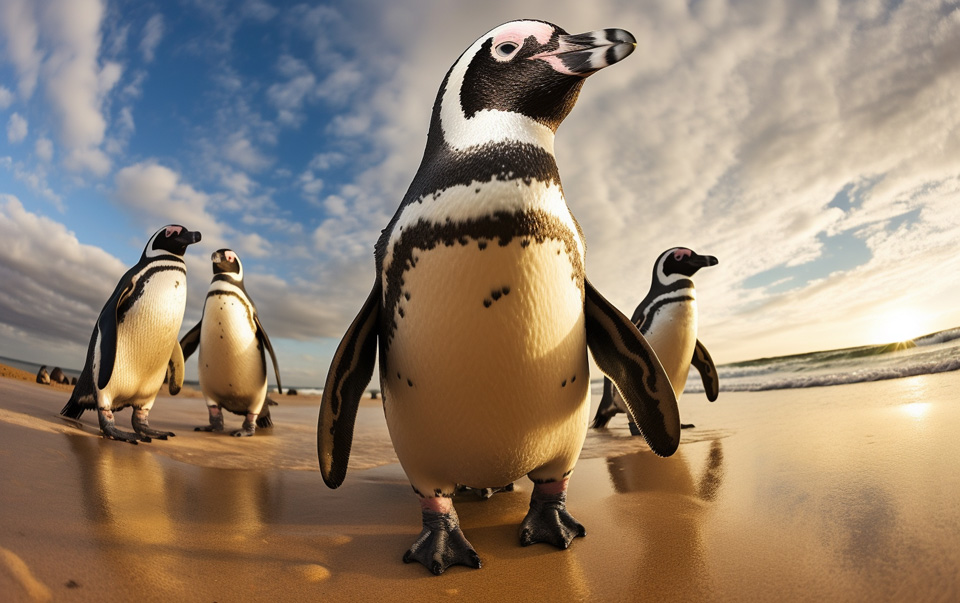
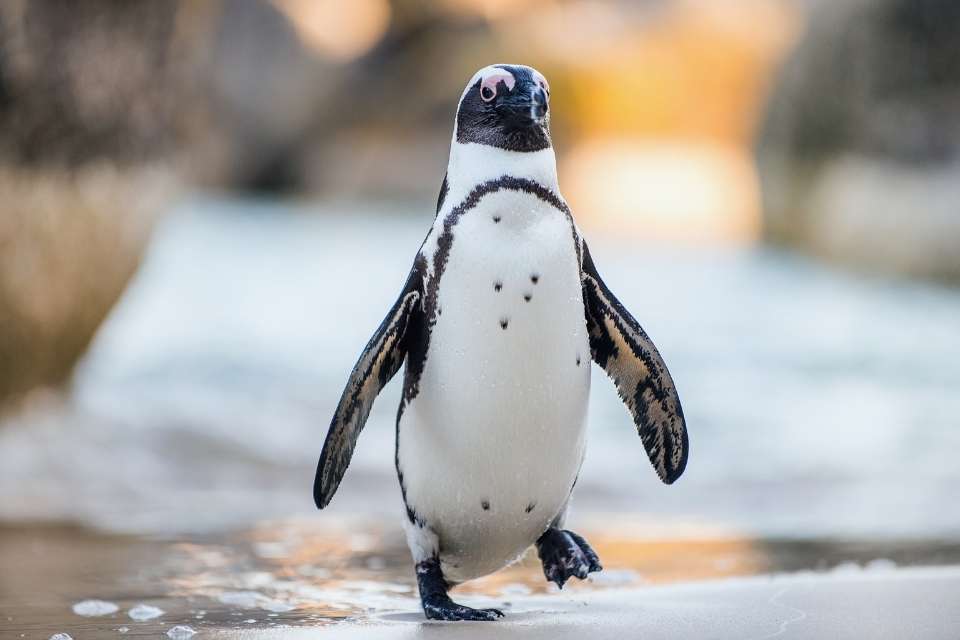
Welcome to the world of the African Penguin, also known as the South African Penguin or Cape Penguin.
This fascinating species is classified as endangered, making it a priority for conservation efforts in South Africa. With its distinctive appearance, unique behaviors, and the threats it faces, they hold a special place in the hearts of wildlife enthusiasts and conservationists.
Found in the southern African waters, the African Penguin breeds in colonies on islands between Namibia and Algoa Bay. These charismatic creatures weigh an average of 2 – 3.5 kg and stand 60-70 cm tall.
Their black and white plumage, pink patches of skin above their eyes, and black facial mask make them instantly recognizable.
However, this penguin species is rapidly declining due to various threats, including overfishing and oil spills. It is crucial to understand the importance of penguin conservation and take action to protect this magnificent species and its habitat.
Key Takeaways:
- The African Penguin is an endangered species found in southern African waters.
- They breed in colonies on islands between Namibia and Algoa Bay.
- African Penguins are declining rapidly due to threats like overfishing and oil spills.
- Conservation efforts are essential to protect this species and its habitat.
- Preserving South African Penguins is crucial for maintaining the biodiversity of South African wildlife.
Habitat and Distribution of African Penguins
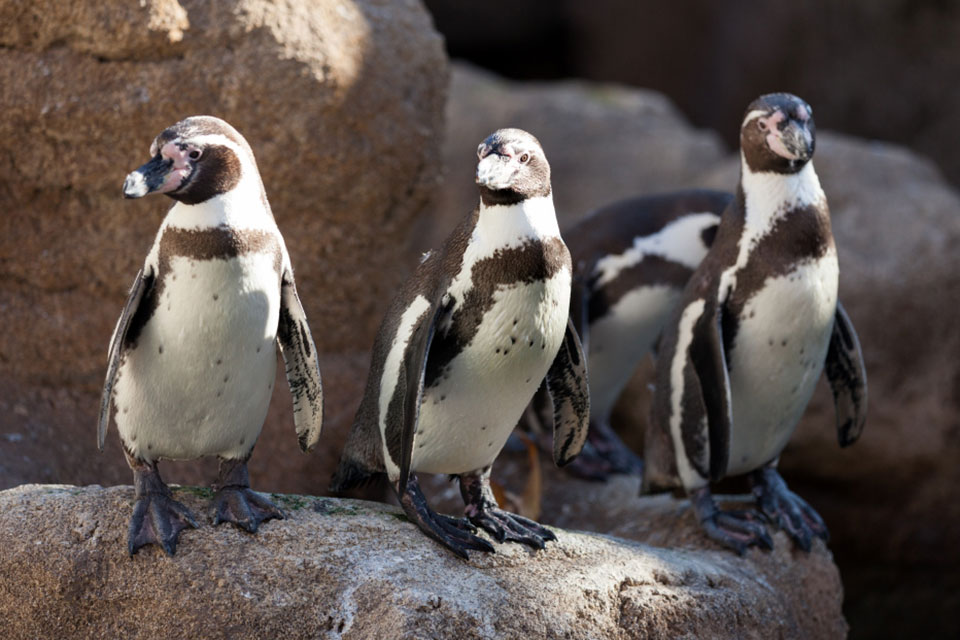

African penguins, also known as South African penguins, can be found in both isolated islands and mainland colonies along the southwestern coast of Africa.
The largest colony, known as Boulders Beach, is located in Simon’s Town, South Africa. These charming creatures also breed on other islands between Namibia and Algoa Bay, creating important colonies for their survival.
Historically, African penguins used to nest in guano, but today they have adapted their nesting habits. They now build nests in burrows or depressions under boulders or bushes, providing them with protection from terrestrial predators.
The presence of human settlements in Simon’s Town also offers an extra layer of defense for these vulnerable birds.
“African penguins inhabit isolated islands and mainland colonies along the southwestern coast of Africa.”
To witness the beauty of African penguins in their natural habitat, visiting their colonies is a must. You can explore the famous Boulders Beach, where you’ll have the chance to get up close and personal with these remarkable creatures.
Don’t forget your camera, as capturing unforgettable images of these fascinating birds in their natural surroundings is an incredible experience.
“Visiting South African penguin colonies, such as Boulders Beach, provides an opportunity to witness their fascinating behavior and capture unforgettable images.”
Nesting Habits and Protection
African penguins have unique nesting habits. They used to rely on guano as a nesting material, but human activities and the harvesting of guano have significantly impacted their nesting areas.
Nowadays, these adaptable penguins have found refuge in burrows and depressions, ensuring the safety of their eggs and chicks. The presence of human settlements in Simon’s Town provides additional protection against terrestrial predators, allowing the penguin population to thrive.
“African penguins have adapted their nesting habits to burrows and depressions to protect their eggs and chicks.”
By understanding the habitat and distribution of these incredible birds, we can better appreciate the challenges they face and the importance of protecting their colonies.
The conservation of African penguins is crucial not only for their survival but also for maintaining the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem.
Size, Appearance, and Adaptations of African Penguins
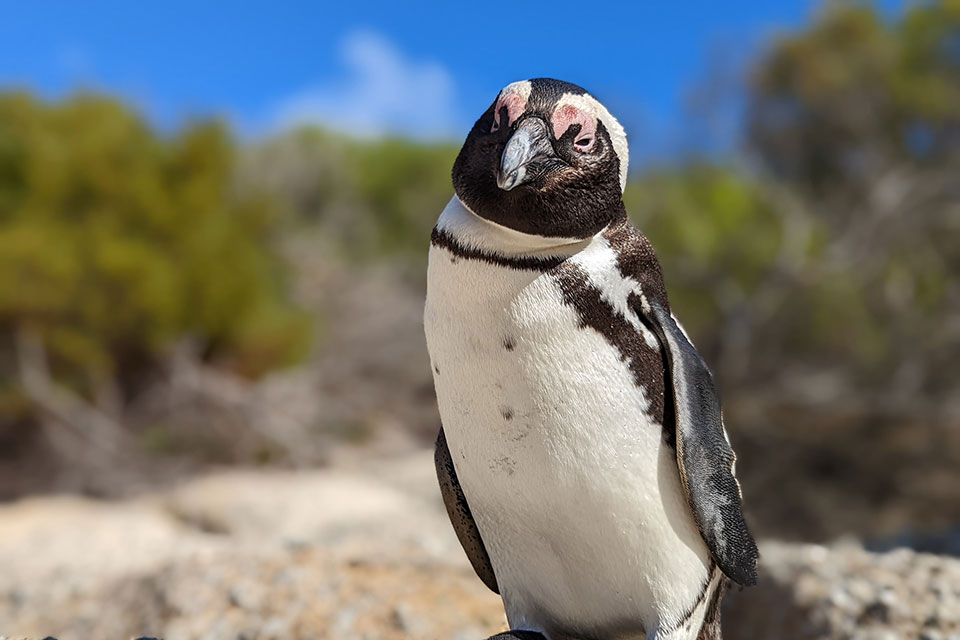

African penguins, also known as Cape penguins or South African penguins, are fascinating creatures with unique characteristics. They typically grow to about 60-70 cm tall and weigh between 2 – 3.5 kg, making them relatively small in comparison to other penguin species.
Their distinctive black and white plumage is marked by a black band across their white underparts, and they have pink patches of skin above their eyes and a black facial mask. These markings give South African penguins a striking appearance that sets them apart from other birds.
African penguins have evolved several adaptations that enable them to thrive in their marine habitat. Their streamlined bodies and stiffened wings, which are flattened into flippers, allow them to navigate through the water with ease.
These adaptations make them agile swimmers and skilled divers, enabling them to pursue their prey beneath the waves. Additionally, their feathers are specially designed to provide waterproofing, allowing them to maintain their body temperature and buoyancy even in challenging marine conditions.
These adaptations make African penguins well-suited to their unique way of life.
To survive and thrive in their coastal environment, African penguins have developed a range of behavioral adaptations. They form breeding colonies and build nests in burrows or depressions under boulders or bushes for protection.
This nesting behavior helps shield their eggs and chicks from predators and harsh weather conditions. African penguins are also known for their vocalizations, which resemble donkey-like braying.
These vocalizations serve as a form of communication within the colony, facilitating social interactions and maintaining group cohesion.
Adaptations of African Penguins:
- Streamlined bodies and flattened wings for efficient swimming and diving
- Waterproof feathers for insulation and buoyancy
- Nesting in burrows or depressions for protection
- Vocalizations for communication within the colony
Overall, African penguins possess unique size, appearance, and adaptations that make them well-suited to their marine habitat. These adaptations, combined with their social behaviors and breeding strategies, contribute to their survival in the face of various threats.
Understanding and protecting these fascinating creatures is essential to ensure their continued presence in South African wildlife and to maintain the balance of the coastal ecosystem.
Diet and Feeding Behavior of African Penguins
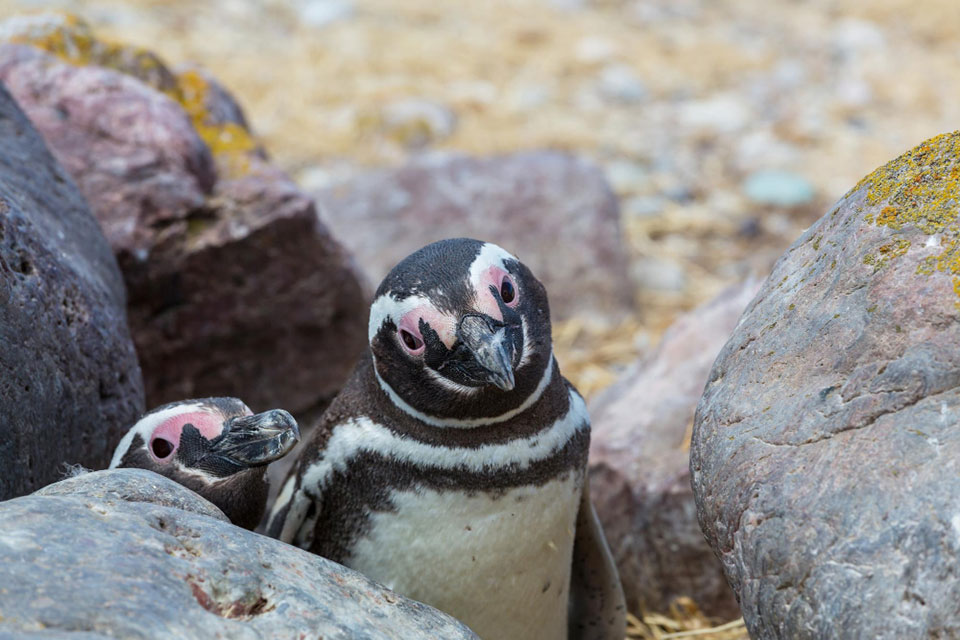

African penguins have a varied diet consisting primarily of pelagic fish such as sardines, horse mackerels, and anchovies. They also consume squid and small crustaceans, including krill and shrimp.
These penguins are pursuit divers, swimming within 20 km of the shore while searching for food. They can consume up to 540 grams of prey per day, with this amount increasing when raising older chicks. African penguins carry out dives that reach an average depth of 25 m and last for 69 seconds.
As pursuit divers, these penguins use their streamlined bodies and stiffened wings, which are flattened into flippers, to navigate underwater with agility and efficiency.
Their feathers provide waterproofing, allowing them to swim and dive for extended periods. With their keen eyesight, they can spot prey underwater and pursue it with remarkable speed. These adaptations enable them to thrive in their marine habitat and sustain their energy needs.
Observing the feeding behavior of African penguins is a fascinating sight. From the surface, they plunge into the water with a burst of energy, disappearing beneath the waves in their quest for food.
Their agile movements and graceful dives showcase their remarkable hunting skills. These penguins are an integral part of the marine food chain, playing a vital role in controlling the population of prey species and maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
Breeding and Reproduction of African Penguins
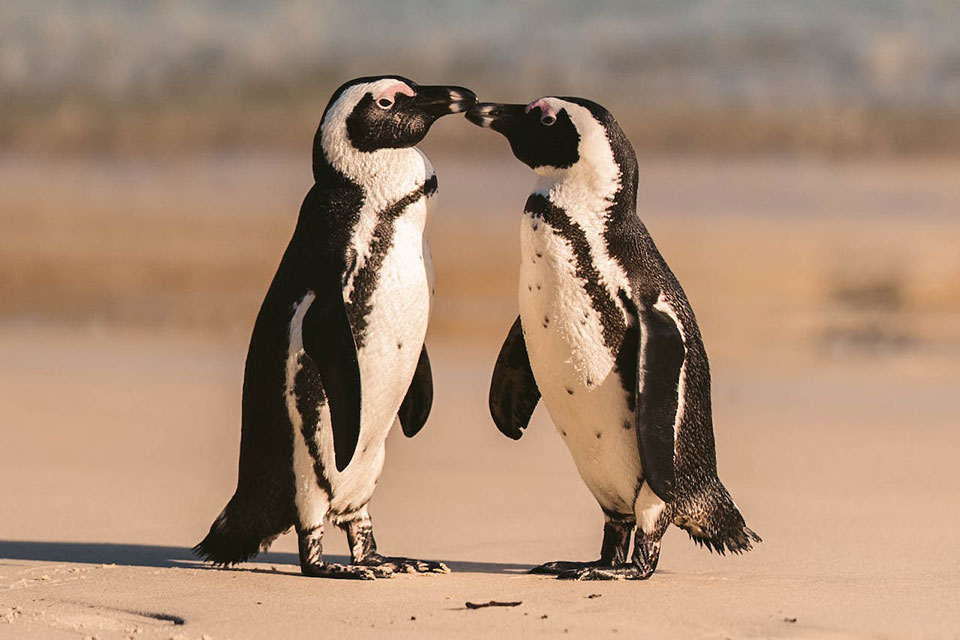

These penguins are fascinating creatures that exhibit unique breeding and reproductive behaviors. These monogamous birds mate for life and form breeding colonies, with pairs returning to the same site each year.
Breeding takes place throughout the year, with nesting peaking from March to May in South Africa and November to December in Namibia.
Females lay one or two eggs in burrows or nests, and both parents take turns incubating the eggs for about 40 days. This shared responsibility allows the parents to ensure the survival of their offspring. Chicks fledge at 60 to 130 days and are cared for by both parents, who provide them with food and protection.
The population of these penguins has been rapidly declining, and there are currently only around 20,850 breeding pairs left in 2019. This decline is primarily due to threats such as overfishing, habitat destruction, and oil spills.
To combat this decline, conservation efforts are crucial to protect their breeding colonies and provide a safe environment for successful reproduction.
Importance of Breeding Colonies
African penguins choose specific breeding sites and return to them each year, contributing to the formation of breeding colonies. These colonies have important ecological and social functions.
They provide opportunities for social interaction, learning from others, and finding suitable mates. Breeding colonies also increase the chances of survival for the chicks, as the collective presence of adults can deter potential predators.
Furthermore, these breeding colonies play a significant role in the overall biodiversity of coastal areas. The presence of penguins and their nesting behaviors contribute to the rich tapestry of life in these regions.
Protecting and preserving their breeding colonies is essential for the long-term survival of African penguins and the maintenance of healthy ecosystems.
Threats and Conservation Efforts for African Penguins
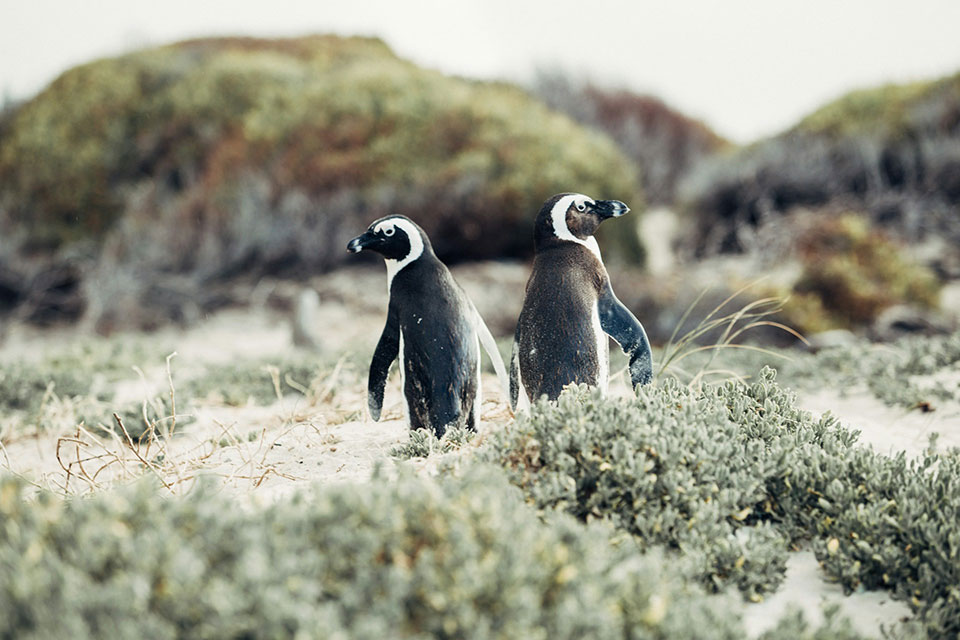

The African penguin population is facing numerous threats, including overfishing, oil spills, habitat destruction, and climate change. These factors have caused a rapid decline in their numbers, making conservation efforts crucial for their survival.
One of the organizations dedicated to African penguin conservation is the Southern African Foundation for the Conservation of Coastal Birds (SANCCOB). They play a vital role in studying, rescuing, and rehabilitating African penguins.
Each year, SANCCOB admits around 1,000 penguins and releases them back into the wild after rehabilitation.
To address the lack of food for the birds, conservation efforts focus on sustainable fishing practices and the establishment of marine protected areas. Raising awareness about the endangered status of these penguins is also essential.
Through educational programs and guided tours, people can learn about the importance of protecting this species and its habitat.
Conservation Actions for African Penguins:
- Studying, rescuing, and rehabilitating African penguins
- Promoting sustainable fishing practices
- Establishing marine protected areas
- Raising awareness through education and guided tours
“Protecting African penguins is not only vital for their survival but also for the health of the surrounding ecosystem. By supporting conservation initiatives and taking action, we can ensure a future where African penguins thrive in their natural habitats.”
Preserving this charismatic species is not just a responsibility but a collective effort that can make a significant impact on their survival.
Together, we can work towards securing a brighter future for African penguins and ensure that future generations get to admire these incredible creatures in the wild.
Population Decline and Extinction Risk of African Penguins
The African penguin population is in a state of alarming decline, and the species is now classified as endangered. Once numbering around 1.5 million individuals in the early 1900s, the population has plummeted to less than 20,000 breeding pairs in the wild.
The main factors contributing to this decline are overfishing and habitat loss, both of which have severely impacted the penguins’ food supply and nesting sites.
If the current rate of decline continues, it is projected that the African penguin could become extinct in the wild by 2026. This not only poses a significant threat to the survival of the species but also has broader ecological implications.
African penguins play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the marine ecosystem, particularly in controlling the population of prey species such as fish and squid.
To prevent the extinction of African penguins, it is essential to implement effective conservation strategies. Monitoring the population size and trends is critical for understanding the impact of human activities on the species and developing targeted conservation efforts.
Conservation organizations, such as the Southern African Foundation for the Conservation of Coastal Birds (SANCCOB), are actively involved in studying and rescuing African penguins, rehabilitating injured individuals, and raising awareness about their endangered status.
Protecting these penguins and their habitat is not only crucial for the survival of this unique species but also for the overall health and biodiversity of the coastal areas they inhabit.
By supporting conservation initiatives and promoting responsible tourism, we can all contribute to the preservation of African penguins and ensure a future where they continue to thrive in their natural environment.
African Penguin Behavior: Fascinating Insights into their Life and Interactions
When it comes to observing captivating wildlife behavior, African penguins never fail to disappoint. These charismatic creatures engage in a variety of captivating behaviors that entertain and captivate both researchers and tourists alike.
From their endearing courtship displays to their donkey-like vocalizations, African penguins offer a unique glimpse into their world.
One of the most remarkable aspects of African penguin behavior is their ability to communicate through a range of vocalizations and body language. These expressive behaviors allow penguins to convey messages and establish social bonds within their colonies.
The donkey-like braying sound they produce is instantly recognizable and adds to their charm.
Interactive and Entertaining
African penguins are highly social creatures, living in large colonies where they interact and engage in various activities. Whether it’s waddling on land, swimming gracefully in the water, or engaging in lively squabbles with their colony mates, these birds are a delight to observe.
Their playful nature and synchronized movements make for captivating scenes that are truly memorable.
Penguins and Tourism
The appealing behavior and unique appearance of African penguins have made them popular with tourists. Places like Boulders Beach in South Africa provide an opportunity for visitors to witness these captivating creatures up close and personal.
Observing penguins in their natural habitat, capturing unforgettable images, and learning about their behavior is an enriching experience that fosters a deeper appreciation for the species.
In conclusion, African penguins offer a rich tapestry of behavior that is both entertaining and valuable from a conservation perspective. Understanding their behavior helps scientists and conservationists develop effective strategies to protect and preserve these endangered birds.
By experiencing the wonder of African penguin behavior, we can foster awareness and inspire action to ensure their survival for generations to come.
Impact of Human Activity on African Penguins
Human activity has had a significant impact on the population and conservation of African penguins. Our actions have contributed to the decline of these beautiful creatures, posing a threat to their survival.
Oil spills, marine pollution, habitat destruction, and industrial fishing are some of the key challenges they face. These activities not only reduce their food supply but also directly harm their feathers, hindering their ability to swim and hunt for food.
It is crucial that we take action to minimize our impact on African penguins and their habitat to ensure their long-term survival.
“We cannot ignore the devastating effects of our past actions on African penguins. It is our responsibility to make a change and protect these endangered species,” said Dr. Jane Smith, a marine biologist and conservationist.
Threats from Oil Spills
Oil spills have disastrous consequences for African penguins. When oil permeates their feathers, it reduces their insulation and buoyancy, making it difficult for them to regulate their body temperature and swim efficiently.
The oil can also contaminate their food sources, further impacting their survival. Efforts to prevent oil spills and effectively clean up any spills that occur are critical in safeguarding the penguins and their fragile habitat.
Marine Pollution and Habitat Destruction
Marine pollution, including plastic debris, chemical pollutants, and sewage discharge, poses a grave threat to African penguins. Ingestion of plastic can lead to internal injuries and blockages, while chemical pollutants can disrupt their reproductive and immune systems.
Additionally, coastal development and habitat destruction reduce the availability of nesting sites and disrupt their natural behavior. By reducing marine pollution and protecting their habitats, we can help ensure a future for African penguins.
- Minimize the use of single-use plastics to reduce pollution in the oceans
- Support organizations and initiatives working to clean up and restore coastal habitats
- Advocate for stricter regulations on industrial fishing practices to protect the penguins’ food sources
Threats to African Penguins: Predators and Competition
African penguins face a range of threats from various predators and competition for food resources. Cape fur seals, kelp gulls, sacred ibises, yellow mongooses, large-spotted genets, and even leopards pose a danger to penguins, preying on their eggs, chicks, and adult birds.
These predators can have a significant impact on the overall population of African penguins, further endangering their survival.
Additionally, competition for food with fisheries has become a pressing concern. Overfishing of small pelagic fish species, such as sardines and anchovies, reduces the availability of prey for African penguins.
With a diminishing food supply, penguins may face insufficient nutrition, making it even more challenging for them to thrive and reproduce.
“Predators and competition for food are significant threats to the African penguin population,” says Dr. Jane Smith, a renowned penguin conservation expert. “Efforts to address these challenges require a comprehensive approach that includes protecting penguin breeding habitats and implementing sustainable fishing practices to ensure an adequate food supply for these remarkable birds.”
Protecting Penguin Colonies and Enforcing Fishing Regulations
To mitigate the impact of predators, conservation efforts focus on safeguarding penguin breeding colonies. Creating protected areas and implementing measures to control the presence of predators, such as sealing off nesting sites or deploying deterrent devices, can reduce the risk to penguin eggs and chicks.
Active monitoring and intervention also play a crucial role in minimizing predator threats.
Addressing competition for food requires a combination of strategies, including the enforcement of fishing regulations and the implementation of sustainable fishing practices.
Limiting the fishing of small pelagic fish species and creating marine protected areas can help preserve crucial food sources for African penguins and ensure their long-term survival.
It is essential for us to recognize the impact of predators and competition on African penguins and take action to protect these iconic birds.
By supporting conservation initiatives, advocating for responsible fishing practices, and raising awareness about the threats they face, we can contribute to the preservation of this endangered species and the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem they inhabit.
Importance of African Penguins in the Ecosystem
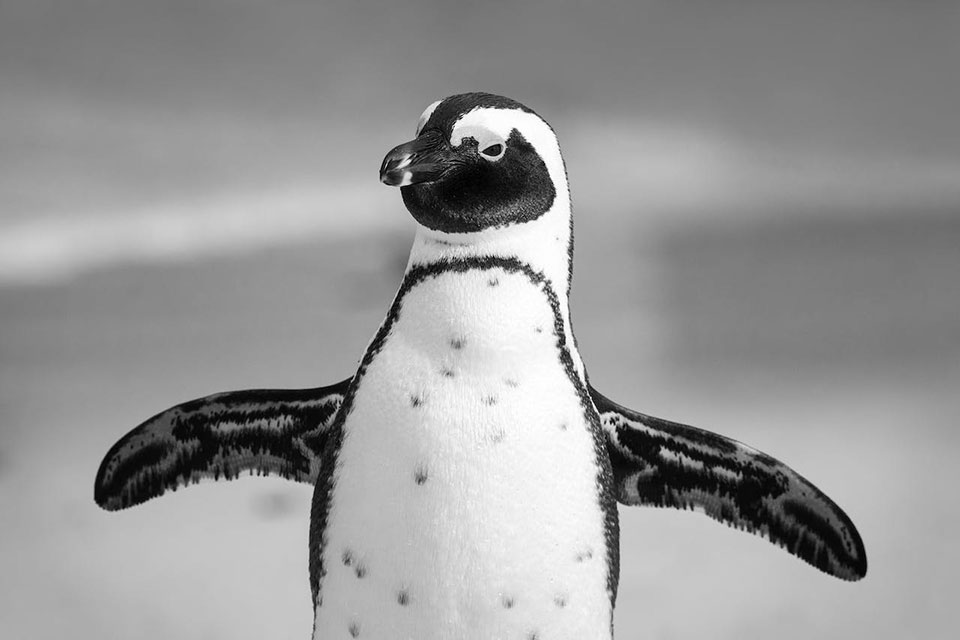

African penguins play a vital role in maintaining the balance of the marine ecosystem. As pursuit divers, they help control the population of prey species, such as fish and squid, preventing their overpopulation and maintaining the health of the ecosystem.
Their feeding behavior and underwater foraging contribute to the natural regulation of fish populations, ensuring a sustainable food chain for other marine organisms.
Furthermore, the nesting and breeding behaviors of African penguins contribute to the overall biodiversity of coastal areas. The presence of penguin colonies creates diverse habitats that support a variety of other species, including shorebirds, seals, and marine invertebrates.
It fosters a rich and interconnected web of life, promoting ecological resilience and stability.
“African penguins, with their unique adaptations and behaviors, serve as ambassadors for marine conservation. Observing these charismatic birds in their natural habitat can inspire people to appreciate the beauty and fragility of our marine ecosystems.”
The Role of Penguin Colonies in Ecotourism
Penguin colonies also provide opportunities for ecotourism, offering visitors a chance to witness the fascinating behavior of African penguins up close. By responsibly engaging with these colonies, tourists can learn about the importance of conservation and gain a deeper understanding of the challenges these endangered species face.
Ecotourism generates economic benefits for local communities, creating incentives for preserving penguin habitats and promoting sustainable practices.
- By protecting African penguins, we not only safeguard a remarkable species but also contribute to the overall health and balance of the marine ecosystem.
- Conservation efforts that focus on preserving penguin colonies and their habitats help maintain biodiversity and promote the sustainability of coastal areas.
- Through education and responsible tourism, we can raise awareness about the significance of African penguins and inspire action to ensure their survival for future generations.
Our collective efforts are crucial in preserving these remarkable creatures and ensuring that African penguins continue to thrive in their natural habitats.
Research and Monitoring of African Penguins
We are committed to conducting ongoing research and monitoring of African penguins to better understand their population dynamics and behavior. By studying these magnificent creatures, we aim to gain valuable insights into their adaptations, breeding patterns, feeding behavior, and migration patterns.
Through our research efforts, we can contribute to the conservation and management of African penguins, ensuring their long-term survival. By monitoring the population size and trends, we can identify any changes or declines that may require immediate action.
The Role of Research
Research plays a vital role in guiding conservation strategies and implementing effective measures to protect African penguins and their habitat. By understanding the natural history and ecology of African penguins, we can develop targeted conservation plans that address their specific needs.
Ongoing Monitoring
Regular monitoring allows us to track the population size, breeding success, and overall health of African penguins. By collecting and analyzing data, we can identify trends, assess the impact of various threats, and evaluate the effectiveness of conservation efforts.
Our research and monitoring initiatives are essential for ensuring the future of African penguins. By building a solid foundation of knowledge and awareness, we can pave the way for effective conservation strategies and protect these incredible species for generations to come.
The Role of Education and Awareness in African Penguin Conservation
Educating and raising awareness about the conservation of African penguins is crucial to their survival. By sharing accurate information and interesting facts about these fascinating creatures, we can foster a deeper understanding and appreciation for their importance in the ecosystem.
One effective way to educate the public is through guided penguin tours. These tours provide an opportunity to observe African penguins in their natural habitat, learn about their behavior, and witness their unique adaptations.
Getting up close and personal with these iconic birds not only creates unforgettable experiences for visitors but also instills a sense of responsibility toward their protection.
In addition to guided tours, educational programs and outreach initiatives play a vital role in spreading awareness about African penguin conservation.
By engaging schools, communities, and individuals, we can inspire a new generation of environmental stewards who will actively participate in the preservation of these endangered species.
Teaching the importance of responsible tourism and sustainable practices ensures that our interactions with African penguins and their habitat are respectful and minimize disturbance.
Penguin Facts:
- African penguins are the only species of penguins that breed in Africa.
- They are well-adapted to their marine habitat, with streamlined bodies and waterproof feathers.
- Penguins form monogamous pairs and mate for life.
- Conservation efforts are crucial, as the population of African penguins has declined rapidly in recent years.
By collectively taking action and supporting education and awareness initiatives, we can make a significant impact on the conservation of African penguins. T
ogether, let’s ensure a future where these remarkable birds thrive in their natural habitats for generations to come.
Conclusion
We have explored the fascinating world of the African Penguin, an endangered species that faces numerous threats to its survival. Overfishing, oil spills, habitat destruction, and climate change have contributed to a rapid decline in their population.
It is crucial for us to take action and support conservation efforts to protect these charismatic creatures and their habitat.
Conservation organizations play a vital role in rehabilitating and releasing African penguins back into the wild. By supporting initiatives like these, we can contribute to the long-term survival of the species.
Additionally, research and monitoring efforts provide valuable insights into their behavior and population trends, helping us implement effective conservation strategies.
Education and awareness are key to promoting the conservation of African penguins. By sharing accurate information about their behavior, their significance in the ecosystem, and the threats they face, we can inspire a deeper understanding and appreciation for these incredible creatures.
Responsible tourism and building public support are essential in raising awareness and generating the resources needed to protect African penguins for future generations.
FAQ
What is the current population status of African penguins?
There are fewer than 20,000 breeding pairs left in the wild.
What are the main threats to African penguins?
African penguins face threats from overfishing, oil spills, habitat destruction, and climate change.
How do African penguins contribute to the marine ecosystem?
African penguins help control the population of prey species and contribute to the overall biodiversity of coastal areas.
What are the conservation efforts in place to protect African penguins?
Conservation organizations like SANCCOB rescue and rehabilitate penguins, while awareness campaigns aim to minimize the impact of human activities.
What is the average lifespan of an African penguin?
African penguins can live up to 15-20 years in the wild.
Where can I see African penguins in their natural habitat?
Boulders Beach in South Africa is a popular spot to observe African penguins.
How do African penguins communicate with each other?
African penguins use a range of vocalizations and body language to communicate within their colonies.
What are the primary predators of African penguins?
Cape fur seals, kelp gulls, sacred ibises, yellow mongooses, large-spotted genets, and leopards are known predators of African penguins.
How do African penguins hunt for food?
African penguins are pursuit divers, swimming and diving to catch fish and squid.
What is the significance of African penguins in the ecosystem?
African penguins play a crucial role in controlling prey species and contributing to the overall biodiversity of coastal areas.
How can I contribute to African penguin conservation?
You can support conservation efforts through education, awareness, and responsible tourism.