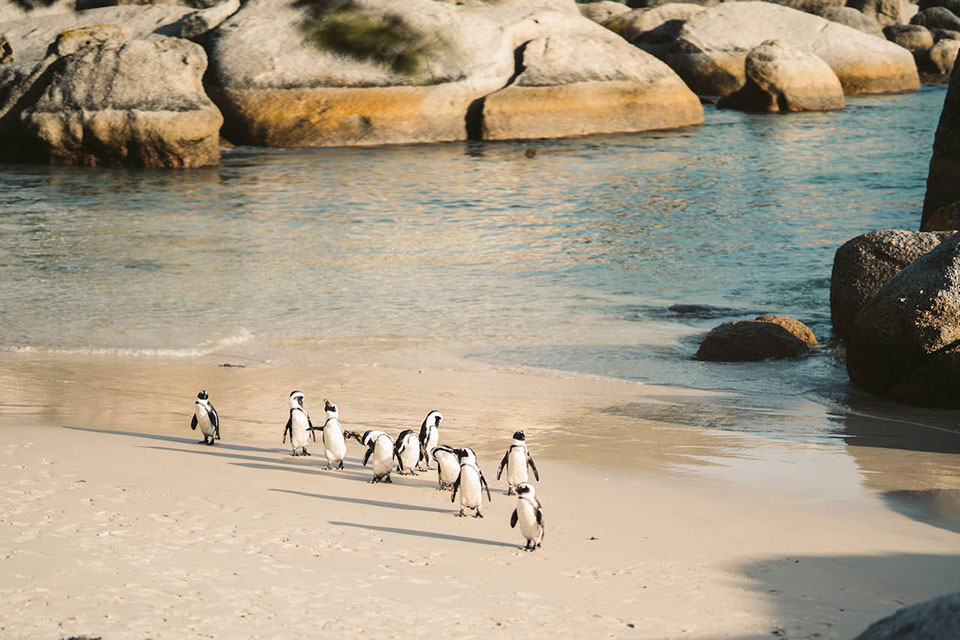
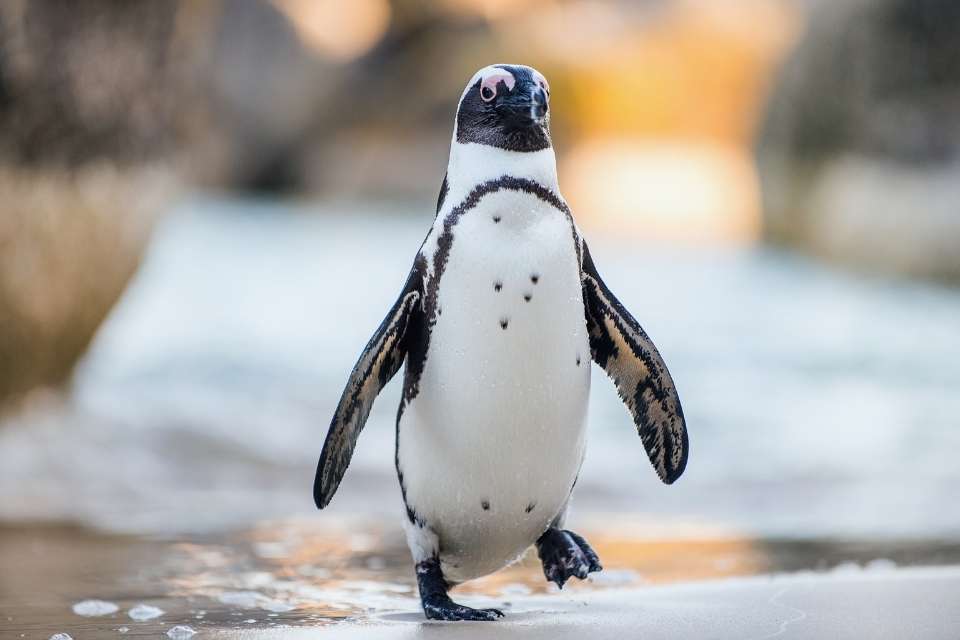
African penguins, also known as Cape penguins or South African penguins, are a species of flightless birds confined to southern African waters.
They are known for their distinctive appearance, with pink patches of skin above the eyes and a black facial mask. While African penguins are found along the coast of South Africa and Namibia, the question remains: do they migrate?
Let’s explore the migration habits of these fascinating birds.
Key Takeaways:
- African penguins exhibit migratory behavior, dispersing along the coastline of southern Africa outside of the breeding season.
- Their migration serves the purpose of finding food resources and avoiding competition in their breeding colonies.
- The exact migration routes of African penguins are not fully understood, but they primarily migrate along the coastline of southern Africa.
- African penguins are pursuit divers that feed primarily on fish and squid, adapting to their marine habitat.
- Conservation efforts and raising awareness are crucial for the long-term survival of African penguins as an endangered species.
African Penguin Migration Behavior
When it comes to African penguins, migration is an integral part of their behavior. These fascinating birds are known to exhibit migratory habits, dispersing along the coastline of southern Africa outside of the breeding season.
Although the exact reasons for their migration are still being studied, researchers believe that it serves the purpose of finding food resources and avoiding competition in their breeding colonies.
During the breeding season, which typically peaks from March to May in South Africa and November to December in Namibia, African penguins establish nests and breed on rocky ground.
However, outside of this season, they embark on their migratory journeys. Juvenile penguins, in particular, venture further west and north, exploring new territories and expanding their range. This behavior highlights their adaptability and resourcefulness in navigating their marine environment.
As we delve deeper into the understanding of African penguin migration, it is important to note that their exact migration routes are not fully understood. However, their primary migration path spans from Namibia to Algoa Bay in South Africa, with some penguins traveling as far as southern Angola.
Occasionally, vagrants have been sighted off the coasts of Gabon, Congo, and Mozambique, further indicating their coastal range limitations.
Why Do African Penguins Migrate?
“Migration plays a crucial role in the survival of African penguins, enabling them to find food resources and avoid competition in their breeding colonies.
The reasons behind African penguin migration are still being investigated. One theory suggests that the availability of food resources is a major driving force, as they need to venture away from their breeding colonies in search of sustenance.
By dispersing along the coastline, they can access a wider range of prey, including fish and squid, which form the mainstay of their diet.
Migrating also helps African penguins avoid competition for limited resources within their colonies. By spreading out along the coast, they can reduce intra-specific competition, ensuring a more efficient allocation of resources for themselves and their young.
Continued Research and Conservation Efforts
The migration behavior of African penguins is a topic of ongoing research, with scientists striving to uncover more insights into their movements, migration routes, and the ecological factors that influence their decisions.
Understanding their migration patterns will aid in the development of targeted conservation strategies to protect these endangered birds.
It is crucial for us to recognize the importance of conserving the habitat and the ecosystems that African penguins depend on.
By supporting conservation initiatives and raising awareness about their plight, we can contribute to the long-term survival of these remarkable birds and ensure that future generations will continue to marvel at their unique migration behavior.
African Penguin Migration Routes

When it comes to the migration routes of African penguins, there is still much that researchers are working to understand. However, what we do know is that these fascinating birds primarily migrate along the coastline of southern Africa.
They can be found in the waters stretching from Namibia all the way to Algoa Bay in South Africa.
While their main migration range is focused on this coastal area, there have been some extraordinary sightings of African penguins venturing even further.
These intrepid travelers have been observed as far north as southern Angola, and there have been occasional reports of vagrants seen off the coasts of Gabon, Congo, and Mozambique.
It is worth noting that the migration patterns of African penguins indicate that their range is relatively limited compared to other penguin species. However, they still manage to explore a significant portion of the southern African coastline in search of food resources and suitable habitats.
African Penguin Migration Facts
When it comes to the migration of African penguins, there are some fascinating facts to discover. These flightless birds, native to the coastal waters of southern Africa, exhibit unique behaviors and adaptations that help them navigate their environment and survive in the wild.
Adaptability to Marine Habitat
African penguins are pursuit divers, meaning they dive underwater in search of their prey. They primarily feed on fish and squid, swimming within 20 kilometers of the shore.
They have been known to consume up to 540 grams of prey per day, showcasing their impressive hunting abilities.
Deep Diving and Extended Duration
During their migration, African penguins have been recorded diving as deep as 130 meters and for durations of up to 275 seconds. These remarkable depths and durations highlight their ability to adapt to different environmental conditions and find food resources in sometimes challenging circumstances.
“African penguins carry out dives that reach an average depth of 25 meters and can last up to 69 seconds.”
Varied Migration Distance
The actual migration distance of African penguins varies depending on the availability of food resources. While they primarily migrate along the coastline of southern Africa, their range can extend as far as southern Angola, with occasional sightings even further afield in Gabon, Congo, and Mozambique.
Despite their limited range compared to other penguin species, African penguins make the most of their environment to ensure their survival.
- African penguins are pursuit divers, feeding on fish and squid near the shore.
- They dive as deep as 130 meters and for durations of up to 275 seconds.
- Migration routes cover the coastline of southern Africa and can extend to southern Angola.
Understanding the migration facts of African penguins is crucial for the conservation of this endangered species.
By raising awareness about their unique adaptations and the challenges they face, we can work together to ensure the long-term survival of these incredible birds.
Conservation Status and Population Trends
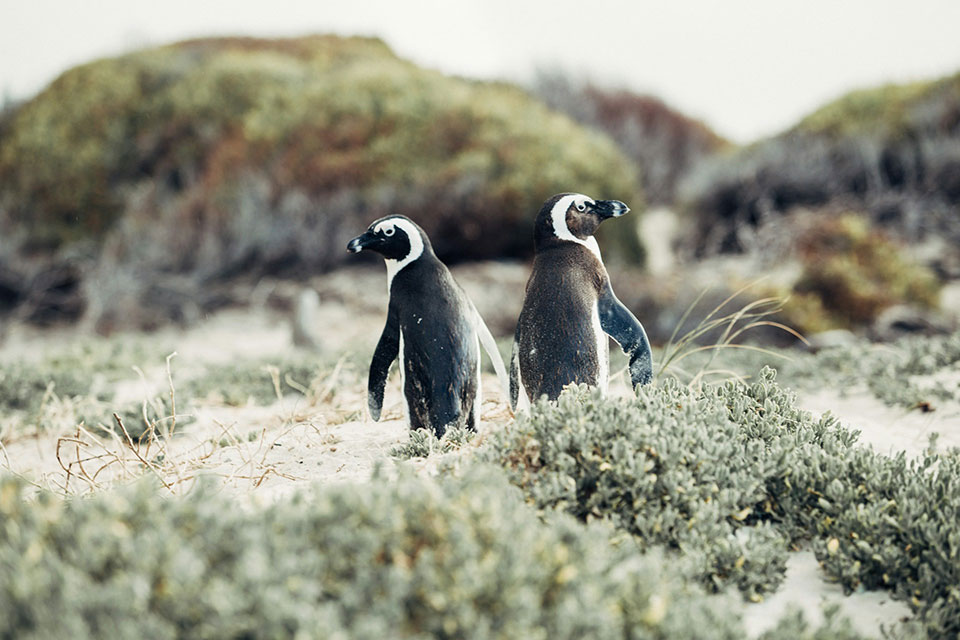

The African penguin population is facing a critical situation, as they are currently classified as endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Over the years, their numbers have rapidly declined, with only 2% of the population that existed in the early 1900s remaining today.
It is a startling statistic that highlights the urgent need for conservation efforts.
Back in 1910, there were approximately 1.4 million adult African penguins. However, by the late 1990s, the global population had plummeted to just 179,000 birds.
Alarming population surveys indicate that African penguins are still on a decline, and if the current trends continue, the species may face extinction in the wild by 2026.
To save these magnificent creatures, dedicated conservation efforts are crucial. One notable example is Boulders Beach in South Africa, which has become a sanctuary for African penguins.
The beach, located near Simon’s Town, is home to a thriving penguin colony that attracts thousands of visitors each year.
Protecting Their Habitats
Conservation initiatives focus on protecting the penguins’ habitats and addressing the various threats they face. Habitat destruction, climate change, oil pollution, and industrial fishing are among the major factors contributing to the decline of African penguins.
By raising awareness about these issues and implementing sustainable practices, we can strive to ensure the survival of these unique birds. Remember, their fate lies in our hands.
Conclusion
In conclusion, African penguins are fascinating birds that exhibit migratory behavior along the coastline of southern Africa. Outside of the breeding season, they disperse in search of food resources, with juvenile penguins venturing further west and north.
While the exact migration routes and reasons behind their behavior are still being studied, migration plays a significant role in their survival.
As an endangered species, African penguins face numerous threats to their existence. Habitat destruction, climate change, oil pollution, and industrial fishing are all contributing factors.
It is crucial that we prioritize conservation efforts and raise awareness about these magnificent birds to ensure their long-term survival.
Places like Boulders Beach, with its thriving penguin colony, offer a valuable opportunity to witness the beauty and uniqueness of African penguins.
By protecting their habitats and supporting conservation initiatives, we can help safeguard the future of this extraordinary species.
FAQ
Do African penguins migrate?
Yes, African penguins exhibit migratory behavior.
What is the migration behavior of African penguins?
African penguins disperse along the coastline of southern Africa outside of the breeding season.
Where do African penguins migrate to?
African penguins primarily migrate along the coastline of southern Africa, spanning from Namibia to Algoa Bay in South Africa.
What are some African penguin migration facts?
African penguins are pursuit divers and can dive as deep as 130 meters and for durations of up to 275 seconds during their migration.
What is the conservation status of African penguins?
African penguins are currently classified as endangered by the IUCN, and their population is declining rapidly.
How can conservation efforts help African penguins?
Conservation efforts, such as those carried out at places like Boulders Beach in South Africa, are crucial for the long-term survival of African penguins.