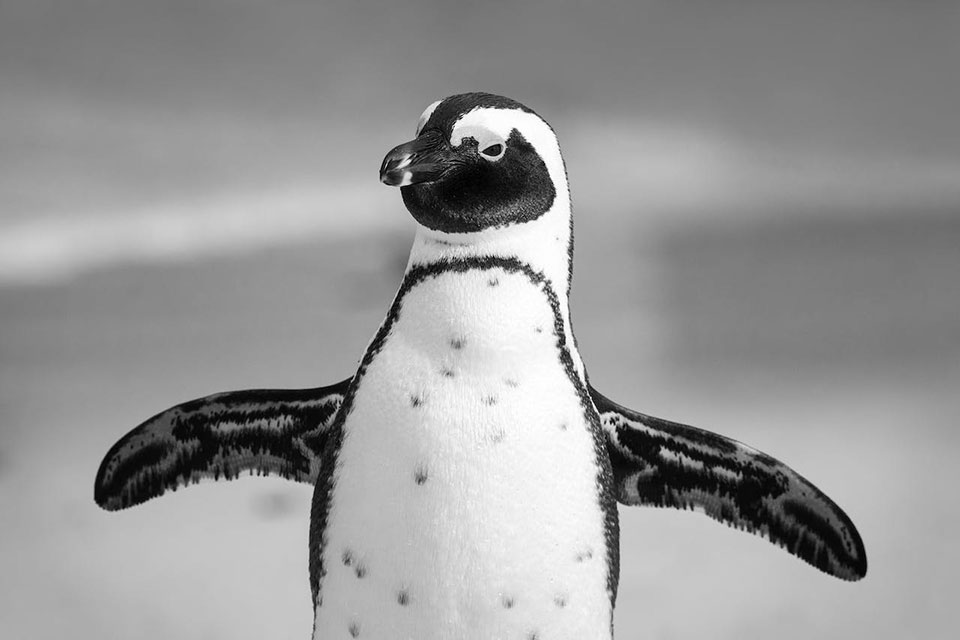
In the coastal areas of southern Africa, a remarkable bird known as the African penguin thrives in both the sea and on land.
With their streamlined bodies, modified wings for swimming, and thick coats of overlapping feathers, these penguins have developed unique survival strategies to adapt to their environment.
However, they face a rapid decline in population due to human-induced threats.
Key Takeaways:
- African penguins have physical adaptations such as streamlined bodies and modified wings for efficient swimming.
- They rely on a thick coat of overlapping feathers for insulation and waterproofing.
- African penguins primarily inhabit coastal islands and prefer sandy or rocky habitats.
- Their diet consists of small pelagic fish, squid, and crustaceans.
- African penguins breed in colonies, laying one to two eggs per clutch and incubating them for approximately 38-41 days.
Physical Adaptations for Survival
African penguins have evolved physical adaptations that enable them to survive and thrive in their coastal habitat.
Their streamlined body shape and modified wings, resembling flippers, make them excellent swimmers, allowing them to navigate through the water with ease. These adaptations enhance their agility and speed, enabling them to catch their prey efficiently.
Their thick coat of overlapping feathers is another vital adaptation. These feathers serve multiple purposes, providing insulation and waterproofing.
The overlapping structure acts as a barrier, preventing water from reaching their skin and keeping them warm in the chilly ocean waters. The feathers also help reduce wind resistance while swimming, enabling them to move swiftly through the water without expending excessive energy.
African penguins have also developed specific behaviors that aid in their survival. They engage in preening, a grooming behavior where they meticulously groom their feathers to maintain their condition and waterproofing.
This behavior helps remove any dirt or debris that may disrupt the insulation and waterproofing properties of their feathers.
Additionally, they often engage in head rubbing and scratching, which not only provides them with comfort but also helps them spread natural oils across their feathers, further enhancing their waterproofing capabilities.
Habitat and Distribution

The habitat of African penguins is primarily along the coastal areas of southern Africa, spanning from Namibia to Algoa Bay in South Africa.
These charismatic birds inhabit various islands along the coast, with two mainland populations found in Betty’s Bay and Boulders Beach near Cape Town. They prefer habitats that offer sandy or rocky sites, with or without vegetation.
The distribution of African penguins is closely tied to the availability of suitable breeding and feeding grounds. They rely on the proximity of their habitats to nutrient-rich waters, where they can find ample food sources.
This is why these penguins are commonly found in areas with upwellings, where cold, nutrient-rich water rises from the deeper ocean depths, creating ideal conditions for fish and other prey species.
African penguins have evolved to thrive in their unique coastal environment, utilizing their physical adaptations to navigate both land and sea.
With their distinctive black and white plumage, these penguins are found in colonies on islands and select mainland sites, creating a spectacle for wildlife enthusiasts and tourists alike.
Feeding Habits

African penguins have specific dietary needs that are essential for their survival. Their food sources primarily consist of small pelagic fish, including pilchards, anchovies, horse mackerel, and herring.
These nutritious fish provide the necessary energy and nutrients for the penguins to thrive. Additionally, African penguins may also consume squid and small crustaceans, which further diversifies their diet.
To obtain their food, African penguins forage at depths of less than 80 meters, venturing up to 40 kilometers away from their breeding colonies. They have the ability to dive and swim underwater in pursuit of their prey.
This hunting behavior allows them to catch fast-swimming fish and other marine organisms that inhabit the same coastal waters.
Key Points:
- African penguins primarily feed on small pelagic fish.
- They may also consume squid and small crustaceans.
- African penguins forage at depths of less than 80 meters.
- They can travel up to 40 kilometers from their breeding colonies in search of food.
“The diet of African penguins is vital to their survival. The availability of their food sources greatly influences their overall health and reproductive success. Changes in fish abundance due to overexploitation and competition with commercial fishing pose significant threats to the penguins’ food resources.”
The food sources for African penguins are critical for their survival, and any disruption in the availability of these resources can have severe consequences for their population.
Conservation efforts that focus on protecting their feeding grounds and managing fisheries sustainably are vital in ensuring the continued survival and well-being of these charismatic birds.
Breeding and Life Cycle
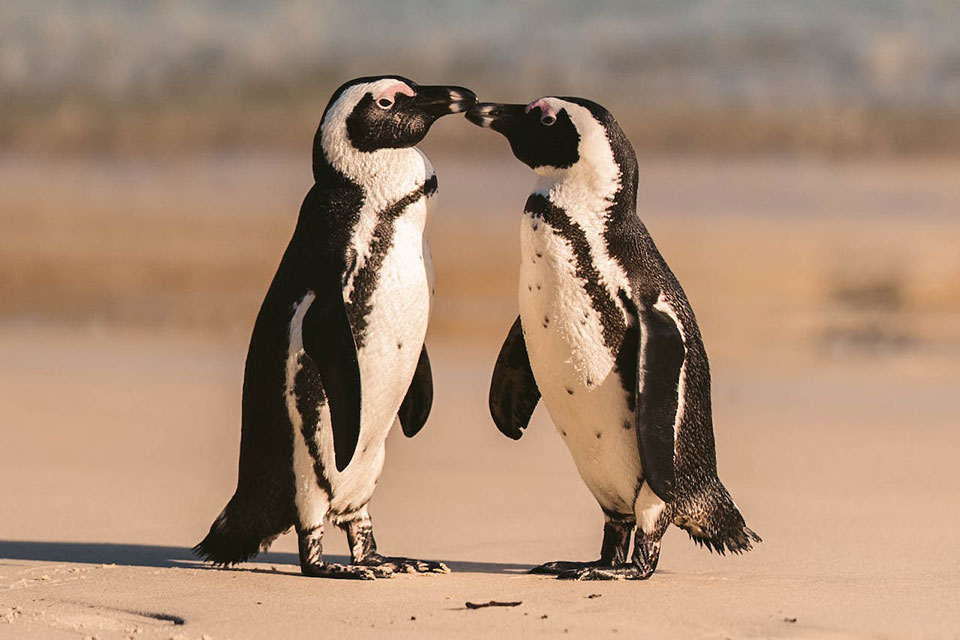

African penguins have fascinating breeding habits that contribute to their survival in their coastal habitat. They form colonies on rocky shore islands where they excavate nests in guano layers or use alternative nesting places such as burrows in sandy soil or crevices between rocks.
This nesting behavior provides them with protection from predators and the elements.
During the breeding season, African penguins lay one to two eggs per clutch. Both parents take turns incubating the eggs, with shifts lasting for about 38-41 days.
This shared parenting ensures that the eggs receive optimal warmth and care. Once the chicks hatch, they are brooded by their parents for the first 15 days. The parents regurgitate food directly from their beaks to feed their young, ensuring their nourishment and growth.
As the chicks grow, they become more independent and start to explore their surroundings. After approximately three months, they are ready to fledge and venture out into the ocean.
At this stage, they are capable swimmers and begin to develop the necessary skills to forage and survive on their own. African penguins reach sexual maturity between four and six years of age, at which point they can partake in the breeding cycle and contribute to the stability of their population.
Predators and Threats
African penguins face various threats from both natural predators and human activities, which have contributed to their declining population. Let’s take a closer look at some of the main predators and threats they encounter:
- Predators at Sea: Cape fur seals, sharks, and killer whales are the primary predators of African penguins in the ocean. These predators hunt the penguins while they are swimming and can pose a significant threat to their survival.
- Predators on Land: On land, African penguins face threats from predators such as mongoose, Cape genets, domestic cats, and even leopards. These predators target penguin chicks, eggs, and adult penguins, especially when they are nesting in colonies.
- Competition with Other Seabirds: African penguins also have to compete with other seabirds for breeding space on their preferred islands and coastal areas. As these habitats become overcrowded, it can limit the availability of suitable nesting sites for penguins.
- Human-Induced Threats: The biggest threats to African penguins come from human activities. Overexploitation of their eggs and guano for commercial purposes has had a significant impact on their population. Habitat modification, pollution, and oil spills also pose serious dangers to their survival. Furthermore, competition for food resources with commercial fishing has led to the decline in their food sources, making it harder for penguins to find enough food to survive.
It is crucial that we address these threats and take immediate action to protect African penguins. By implementing conservation measures, raising awareness, and supporting research, we can work towards securing the future of these beautiful and vulnerable birds.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation of African penguins is of utmost importance to ensure the survival of this endangered species. We are actively involved in various conservation efforts aimed at protecting and restoring their populations.
One key aspect of our conservation strategy is the creation of protected areas. These designated areas provide safe breeding and nesting grounds for African penguins, minimizing disturbances from human activities and predation by other animals.
By safeguarding their habitats, we are helping to maintain the balance of the marine ecosystem they depend on.
Monitoring and research play a crucial role in understanding the dynamics of African penguins and the threats they face. Through scientific studies, we can gather valuable data on their behavior, population trends, and the impact of external factors.
This information guides our conservation efforts, allowing us to implement targeted measures for their protection.
The Conservation Measures Include:
- Restoring and enhancing their habitat: We work to restore and improve nesting sites, ensuring suitable conditions for breeding and raising chicks. This includes removing invasive vegetation, managing predators, and protecting against erosion.
- Public awareness campaigns: Educating the public about the importance of African penguin conservation is vital for their long-term survival. We strive to raise awareness about the threats they face, promote responsible tourism practices, and encourage support for conservation initiatives.
It is through collaborative efforts that we can secure a future for African penguins. By supporting their conservation, we can protect not only these fascinating birds but also the rich biodiversity of our marine ecosystems.
Threats from Climate Change
Climate change poses significant threats to the survival of African penguins. As our planet’s climate continues to shift, these charismatic birds face escalating challenges in their already vulnerable habitat.
Rising sea levels and the increasing frequency and intensity of storms put their nesting sites at risk of destruction. These disturbances disrupt their breeding cycles and affect the overall stability of their populations.
The changing ocean currents and temperatures also impact the availability of food sources for African penguins. As fish and other prey species migrate or decline due to changing conditions, the penguins face food scarcity.
This can lead to malnutrition, reduced reproductive success, and overall population decline.
Additionally, the rising temperatures associated with climate change result in more frequent heatwaves. African penguins, adapted to the cooler coastal climate, struggle in extreme heat.
Heatwaves can cause stress, physiological changes, and increased mortality rates among both adults and chicks. The survival of African penguins is further jeopardized by these heat-related challenges.
Threats from Climate Change:
- Rising sea levels and increased storms
- Disruption of nesting sites and breeding cycles
- Changing ocean currents and temperatures affecting food availability
- Food scarcity leads to malnutrition and reduced reproductive success
- Increased occurrence of heatwaves affecting survival rates
“The changing climate directly impacts every aspect of African penguins’ lives, from their nesting sites to their food sources. Urgent action is needed to mitigate the effects of climate change and protect these vulnerable species.”
It is crucial for us to recognize the threats that climate change poses to African penguins and take immediate action to address these challenges.
Through collective efforts and global initiatives, we can mitigate the impacts of climate change, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and protect the habitats that these beautiful creatures rely on.
By prioritizing conservation efforts and raising awareness about the importance of climate action, we can secure a sustainable future for African penguins and safeguard the biodiversity of our planet.
Tourist Attractions and Education
Boulders Beach near Cape Town is a must-visit destination for those seeking an up-close encounter with African penguins. This picturesque beach is home to a protected penguin colony, offering visitors a unique opportunity to observe these captivating creatures in their natural habitat.
As you stroll along the boardwalks and sandy shores, you’ll find yourself surrounded by the playful antics and distinctive calls of the African penguins. Watching them waddle through the white sand and dive into the sparkling turquoise waters is a truly mesmerizing experience.
Alongside the natural beauty of Boulders Beach, there are also educational programs and initiatives in place to raise awareness about the importance of penguin conservation.
Visitors can learn about the challenges faced by African penguins and gain a deeper understanding of the need to protect these incredible birds and their fragile environment.
Importance of African Penguin Conservation
African penguins are not just fascinating creatures, but they also play a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem.
Their adaptations and behaviors have allowed them to thrive in their coastal habitat, but their survival is now under threat. That is why conservation efforts are crucial to protect these incredible birds and their habitat.
The African penguin’s unique physical adaptations, such as their streamlined body shape and modified wings, enable them to be efficient swimmers. Their ability to control fish and squid populations helps maintain the balance of the marine food chain.
By protecting their habitat and ensuring their survival, we can preserve the biodiversity and overall health of marine ecosystems.
Conservation efforts for African penguins involve creating protected areas, monitoring their populations, and restoring their habitat. Additionally, public awareness campaigns and educational programs play a crucial role in spreading knowledge about these amazing birds and the threats they face.
By engaging individuals, communities, and stakeholders, we can foster a sense of responsibility towards the conservation of African penguins and their environment.
The Importance of Collaboration
- Collaboration between government agencies, conservation organizations, and local communities is essential for effective conservation strategies.
- By working together, we can establish sustainable fishing practices, reduce pollution, and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
- Supporting research initiatives can also provide valuable insights into the behavior, biology, and ecology of African penguins, helping us better understand their needs and develop targeted conservation measures.
With collective efforts, we can ensure that future generations will have the opportunity to witness the unique beauty and importance of African penguins in their natural habitat.
The conservation of these incredible birds is not just about protecting a single species; it is about safeguarding the intricate web of life that thrives in the marine environment, ultimately benefiting us all.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we have explored the incredible survival strategies of African penguins and the challenges they face in their coastal habitat. These charismatic birds have evolved physical adaptations, efficient swimming abilities, and specific behaviors to thrive in their environment.
However, the survival of African penguins is under severe threat due to human-induced factors. Overexploitation, habitat modification, pollution, and climate change have pushed these birds to the brink of extinction.
It is crucial that we take immediate action to protect the African penguin population. By implementing effective conservation measures, raising awareness, and supporting research, we can ensure their survival for future generations.
Together, we can make a difference and safeguard the incredible survival strategies of African penguins against the threats they face.
FAQ
How do African penguins survive?
African penguins have several survival strategies, including physical adaptations, efficient swimming abilities, and specific breeding and feeding behaviors.
What are the physical adaptations that help African penguins survive?
African penguins have a streamlined body shape, modified wings for swimming, and a thick coat of overlapping feathers for insulation and waterproofing.
Where do African penguins live?
African penguins are endemic to the coastal areas of southern Africa, from Namibia to Algoa Bay in South Africa. They primarily inhabit islands along the coast, with two mainland populations in Betty’s Bay and Boulders Beach near Cape Town.
What do African penguins eat?
African penguins mainly feed on small pelagic fish, such as pilchards, anchovies, horse mackerel, and herring. Their diet may also include squid and small crustaceans.
How do African penguins breed and reproduce?
African penguins breed in colonies on rocky shore islands. They lay one to two eggs per clutch, and both parents take turns incubating the eggs for about 38-41 days. Chicks are brooded for the first 15 days and are dependent on their parents for food.
What are the predators and threats to African penguins?
African penguins face predators such as Cape fur seals, sharks, killer whales, mongoose, Cape genets, domestic cats, and leopards. Human activities, including overexploitation, habitat modification, pollution, and climate change, are also significant threats.
What conservation efforts are being made to protect African penguins?
Conservation efforts include creating protected areas, monitoring and research, habitat restoration, and public awareness campaigns.
How does climate change affect African penguins?
Climate change poses threats to African penguins through rising sea levels, increased storms, changes in ocean currents and temperature, and heatwaves affecting their reproductive success and survival.
Are African penguins a tourist attraction?
Yes, African penguins are a popular tourist attraction, especially at Boulders Beach near Cape Town. Tourists can observe and learn about these charismatic birds in their natural habitat.
Why is the conservation of African penguins important?
African penguins play a vital role in the marine ecosystem as top predators, helping control the population of fish and squid. Their conservation is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and the health of marine habitats.
What is the conclusion about African penguin survival strategies and threats?
African penguins have evolved various survival strategies, but human-induced threats have contributed to their endangered status. Conservation efforts are essential to protect these iconic and vulnerable species.