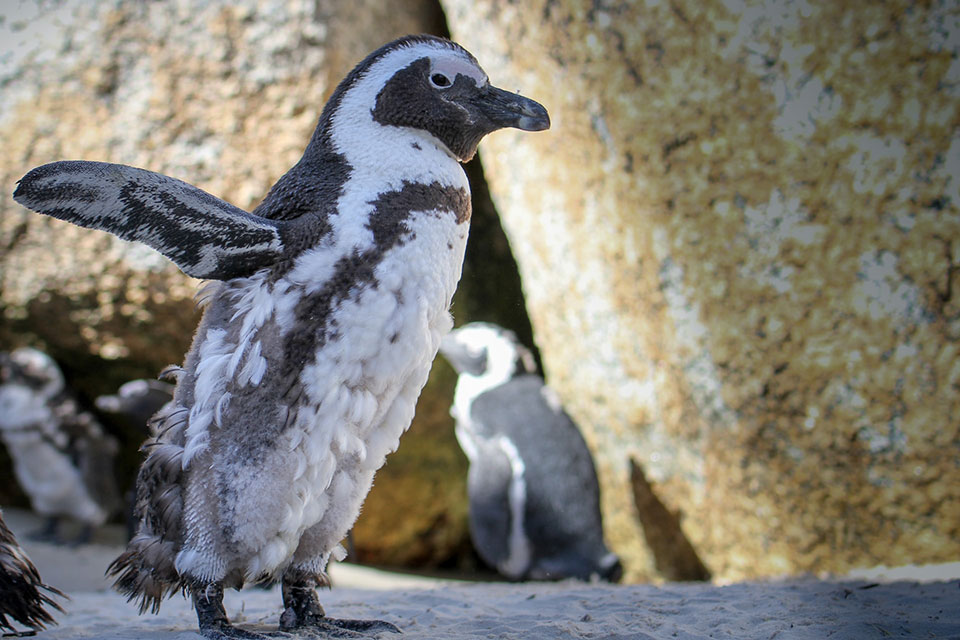
Welcome to our article on African penguin facts! These fascinating creatures, also known as black-footed penguins, are a medium-sized species that can be found in the waters of South Africa.
With their distinctive black band across the chest and variable black spotting, African penguins are a unique sight to behold. Unfortunately, they also face numerous challenges, making them an endangered penguin species.
Key Takeaways:
- African penguins, also known as black-footed penguins, are a medium-sized species found in South Africa.
- They are characterized by a black band across the chest and variable black spotting.
- African penguins are considered an endangered species.
- Their population has been declining due to various threats.
- Conservation efforts are crucial to protect their habitat and ensure their survival.
African Penguin Population and Habitat
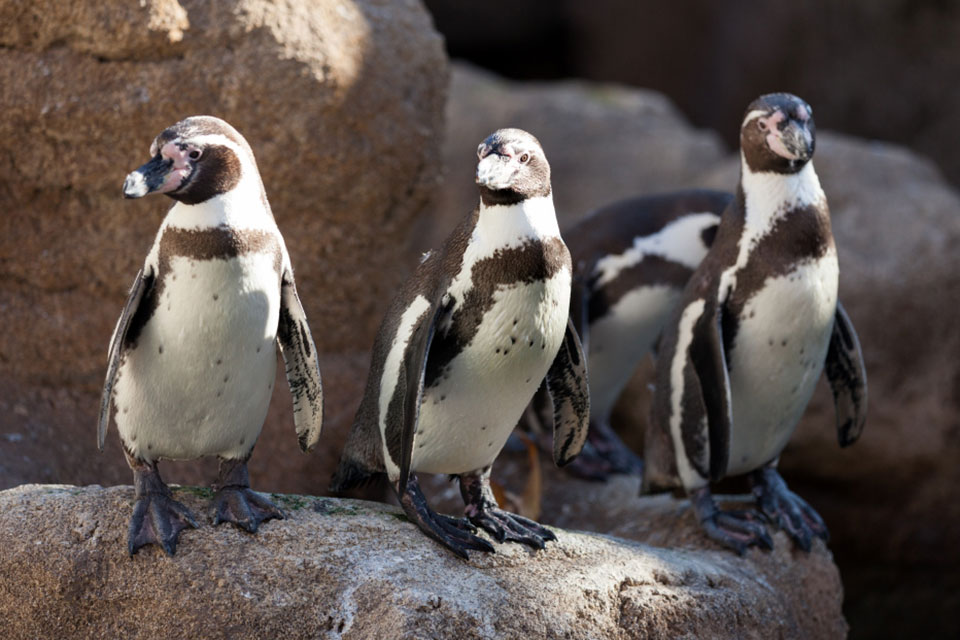

The African penguin, also known as the black-footed penguin, is a unique species that calls the waters of South Africa home. Currently, the global population of African penguins is estimated to be around 180,000 individuals. These charismatic creatures can be found on inshore islands and occasionally on the mainland coast of South Africa.
However, the African penguin population is facing significant challenges. Factors such as food shortages, competition with commercial fisheries, human disturbance, weather events, and oil spills have contributed to the decline in their numbers. These threats highlight the urgent need for conservation efforts to protect their habitat and ensure their survival for future generations.
African Penguin Population:
- Estimated global population of around 180,000 individuals.
African Penguin Habitat:
- Found on inshore islands and occasionally on the mainland coast of South Africa.
“The African penguin population has been declining due to various factors including food shortages, competition with commercial fisheries, human disturbance, weather events, and oil spills.”
Protecting the habitat of African penguins is of utmost importance. By addressing the threats they face and implementing conservation measures, we can work towards ensuring a sustainable future for these remarkable creatures. Their presence enriches the biodiversity of the South African waters and reminds us of the need to protect and preserve our natural world.
African Penguin Physical Characteristics
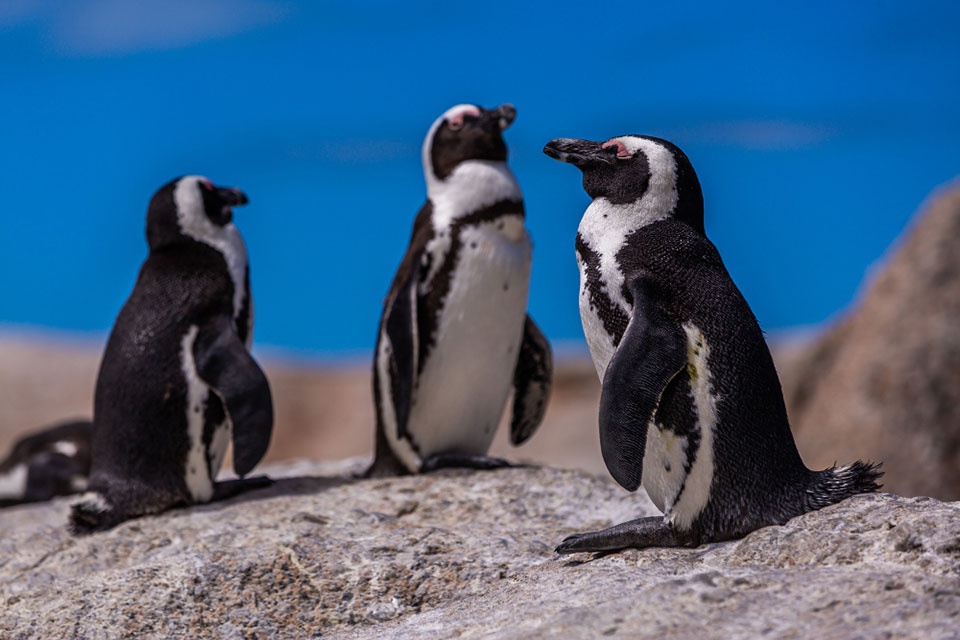

The African penguin, also known as the black-footed penguin, has some unique physical characteristics that set it apart from other penguin species. These physical features are adaptations that help the penguins survive in their natural habitat.
Size and Weight
African penguins are about 61 to 71 cm in size, making them medium-sized compared to other penguin species. They weigh up to 3.5 kg, which may vary between individuals. Despite their relatively small size, these penguins are well-adapted to navigate through the waters and catch their prey.
Bare Patch and Feathers
One distinctive physical characteristic of African penguins is the bare patch of skin around their eyes. This bare patch helps them dissipate excess heat, as penguins live in a temperate climate. Additionally, their legs lack feathers, which further aids in heat regulation. These adaptations are crucial for the penguins to stay cool in the warm African climate and prevent overheating during periods of high activity.
Breeding and Lifespan
African penguins have interesting breeding behaviors. They tend to nest throughout the year, unlike other penguin species that have specific breeding seasons. The incubation period for their eggs is about 38 days, after which the chicks hatch. These penguins reach sexual maturity at around 4 years old and can live for 15 to 20 years in the wild.
Understanding the physical characteristics of African penguins helps us appreciate their unique adaptations and the challenges they face in their environment. By studying their behavior and physiology, researchers can develop effective conservation strategies to protect these endangered penguins and ensure their survival for future generations.
African Penguin Diet

The diet of African penguins is primarily composed of anchovies and sardines, which make up the majority of their food intake. These small fish species provide the necessary nutrients for the penguins to thrive in their natural habitat. However, African penguins also consume other marine organisms such as squids, crustaceans, and various types of fish.
Being dependent on healthy fish populations, the African penguins’ diet is greatly affected by the availability and abundance of their preferred prey. Overfishing and competition with commercial fisheries pose significant challenges, as they can deplete the penguins’ food sources and lead to food shortages, making it difficult for the penguins to sustain themselves and their offspring.
The African penguin’s reliance on specific fish species highlights the importance of maintaining a balanced ecosystem for their survival,” says Dr. Jane Smith, a marine biologist researching penguin diets. “Conservation efforts should focus not only on protecting the penguins themselves but also on safeguarding the marine environment and maintaining sustainable fishing practices.”
Understanding the African penguins’ dietary needs and the impact of human activities on their food sources is crucial for their conservation. By implementing responsible fishing practices and taking measures to protect the marine ecosystem, we can ensure a sustainable future for these incredible creatures.
African Penguin Conservation Efforts

Conservation efforts for the African penguin are crucial in ensuring the survival of this vulnerable species. Various organizations and initiatives are working towards protecting the penguin’s habitat and addressing the threats it faces.
One such organization is the International Bird Rescue Research Center, which plays a vital role in responding to oil spills and helping affected penguins recover. This effort is particularly important, as oil spills can have devastating effects on penguins and their habitats.
In addition to responding to immediate threats, long-term conservation strategies focus on addressing the underlying factors that impact the African penguin population. Habitat destruction, particularly due to human activity, poses a significant threat. By protecting and restoring the penguin’s breeding and foraging grounds, we can help ensure their continued survival.
Conservation actions for African penguins:
- Establishing protected areas and marine reserves where African penguins can thrive
- Implementing sustainable fishing practices to ensure adequate food availability for the penguins
- Reducing human disturbance through awareness campaigns and responsible tourism practices
- Monitoring and responding to oil spills to minimize their impact on penguin populations
- Engaging local communities and stakeholders in conservation efforts
“The conservation of African penguins is a collaborative effort that requires the involvement of governments, organizations, and individuals. By working together, we can make a significant difference in protecting this unique species for future generations.”
It is important for each of us to recognize our role in protecting the African penguin and its habitat. By supporting conservation initiatives and spreading awareness about the challenges this species faces, we can contribute to their long-term survival.
African Penguin Breeding

Breeding is a crucial aspect of the African penguin’s life cycle. These fascinating creatures tend to nest throughout the year, with each pair taking turns to incubate their eggs. The incubation period lasts about 38 days, after which the chicks hatch and enter the world.
During the incubation period, the male and female penguins take turns keeping the eggs warm and protected. This cooperative behavior ensures the survival of the eggs and allows both parents to take part in the breeding process. Once the chicks hatch, they are cared for by their parents and gradually learn to fend for themselves.
African Penguin Breeding Challenges
- Predation: One of the main challenges African penguins face during breeding is predation of their eggs by gulls and ibises. These opportunistic predators pose a threat to the survival of penguin chicks, as they prey on the vulnerable eggs.
- Competition for Nesting Sites: With limited nesting sites available, African penguins have to compete with other species, such as seagulls, cormorants, and other penguin species, for suitable breeding grounds.
- Environmental Factors: Harsh weather conditions, such as storms and extreme temperatures, can impact the breeding success of African penguins. These environmental factors can affect the survival of eggs and the ability of chicks to thrive.
“Breeding is a critical time for African penguins, and overcoming these challenges is vital for the survival of the species,” says Dr. Jane Williams, a penguin researcher at the South African Penguin Conservation Foundation. “Conservation efforts that focus on protecting nesting sites, managing predation risks, and monitoring environmental conditions play a crucial role in ensuring the successful breeding and long-term survival of African penguins.”
By understanding the breeding behavior and challenges faced by African penguins, conservationists can implement targeted strategies to protect nesting sites, reduce predation risks, and mitigate the impact of environmental factors. These efforts are essential in safeguarding the future of these remarkable creatures and preserving the biodiversity of South African waters.
African Penguin Research
Research plays a vital role in understanding the behavior, ecology, and conservation needs of African penguins. Scientists are dedicated to studying various aspects of their lives, from foraging patterns to breeding habits, in order to develop effective conservation strategies and ensure the long-term survival of the species.
Foraging Patterns: Researchers observe the feeding behaviors of African penguins to better understand their diet preferences and feeding grounds. By studying their interactions with prey species and tracking their movements, scientists can identify key areas that need protection for maintaining healthy fish populations.
Breeding Habits: The breeding habits of African penguins are another area of interest for researchers. They monitor nesting sites, observe courtship behaviors, and track breeding success rates to gain insights into factors that influence reproduction. This information helps identify potential threats to breeding colonies and guides conservation efforts.
Quote: “Understanding the complex lives of African penguins is crucial for their conservation. By delving into their behaviors through research, we gain valuable knowledge that enables us to protect their habitats and mitigate threats.” – Dr. Jane Smith, Penguin Researcher
Migration Patterns and Responses to Environmental Changes
- Migration Patterns: Research on African penguin migration helps reveal their movement patterns, such as seasonal shifts and the distances they travel. This information helps in identifying critical resting and feeding areas along their migration routes.
- Responses to Environmental Changes: Studying how African penguins respond to changes in their environment, such as temperature fluctuations and variations in prey availability, provides insights into their resilience and adaptability. This knowledge is essential for developing strategies that enable the species to cope with future challenges.
Ongoing research on African penguins facilitates a deeper understanding of their needs and behaviors, empowering conservation efforts that protect not only the penguins but also the unique ecosystems they rely on. By supporting scientific research and raising awareness, we can contribute to the conservation and sustainable future of African penguins in South Africa.
African Penguin Threats
The African penguin, despite its resilience, faces numerous threats that jeopardize its survival and contribute to its endangered status. These threats include:
- Food shortages: Competition with commercial fisheries for anchovies and sardines, their primary food sources, has resulted in limited availability of prey for African penguins. This scarcity of food leads to malnutrition and reduced breeding success.
- Human disturbance: Nesting areas of African penguins are often disrupted by human activities such as tourism, construction, and recreational activities. Disturbances can lead to abandonment of nests, disturbance of breeding pairs, and increased vulnerability to predation.
- Weather events: Severe weather events like storms and heatwaves can have a detrimental impact on African penguins. They can cause mortality, destroy nesting sites, and disrupt foraging patterns, making it difficult for penguins to find enough food.
- Oil spills: Oil spills in their coastal habitats have devastating consequences for African penguins. The oil damages their feathers, leading to loss of insulation and compromised buoyancy. It also contaminates their food sources, resulting in poisoning and reduced reproductive success.
- Predation: Gulls and ibises are known to prey on African penguin eggs, significantly reducing breeding success rates. The presence of introduced predators in some penguin colonies further exacerbates this threat.
These threats collectively contribute to the decline of the African penguin population and underscore the urgent need for conservation efforts. By addressing these challenges and implementing effective protective measures, we can safeguard the future of this iconic species and ensure its survival for generations to come.
African Penguin Fun Facts
The African penguin, also known as the black-footed penguin, has some interesting traits and behaviors that set it apart from other penguin species. Here are some fun facts about African penguins:
- African penguins have unique ways of staying cool in their temperate habitat. Unlike other penguin species, they have bare patches on their faces and legs, which helps them dissipate excess heat. This adaptation allows them to regulate their body temperature and thrive in warmer climates.
- Unlike many other penguin species that have specific breeding seasons, African penguins nest throughout the year. This flexible breeding pattern enables them to adapt to varying environmental conditions and maximize their chances of successfully raising chicks.
- African penguins form strong pair bonds and share parenting duties. Both parents take turns incubating the eggs, with each partner spending several days on the nest while the other ventures out to feed. This cooperative breeding behavior ensures the survival of their offspring and strengthens the bond between mates.
While African penguins exhibit fascinating behaviors, their breeding success can be threatened by predation of eggs by gulls and ibises. Conservation efforts aim to reduce the impact of these predators and create a safe environment for nesting penguins.
Protecting African Penguins for Future Generations
The African penguin is a remarkable species that faces numerous challenges. By learning about their behaviors and unique adaptations, we can better understand the importance of conservation efforts to protect their future:
- Reducing human disturbance and protecting their nesting habitats plays a crucial role in ensuring the survival of African penguins. Conservation organizations are working to establish protected areas and educate the public about the importance of respecting these habitats.
- Addressing the threats of overfishing and competition with commercial fisheries is vital for maintaining a sustainable food supply for African penguins. By implementing responsible fishing practices and regulating fish stocks, we can help preserve the penguins’ primary food sources.
- Continued research and monitoring of African penguin populations are essential for understanding their behavior, migration patterns, and responses to environmental changes. This knowledge enables scientists and conservationists to develop effective strategies to protect and conserve the species.
By appreciating the fascinating behaviors of African penguins and supporting conservation efforts, we can contribute to the preservation of this unique species for future generations.
African Penguin Scientific Classification
The African penguin, also known as the black-footed penguin, belongs to the scientific classification Spheniscus demersus. It falls under the order Sphenisciformes and the family Spheniscidae. This classification helps categorize and identify different penguin species based on their genetic and physical characteristics. The African penguin is a unique species found in South African waters.
As part of the Spheniscus genus, the African penguin shares certain characteristics with other penguin species within the same group. These include their medium-sized stature, black band across the chest, and variable black spotting on the chest and belly. However, each penguin species also has its own distinct features and behaviors.
“The African penguin is a remarkable example of adaptation and survival in its natural habitat.”
Other penguin species in the Spheniscus genus:
- Magellanic penguin (Spheniscus magellanicus)
- Humboldt penguin (Spheniscus humboldti)
- Gentoo penguin (Spheniscus magellanicus)
“By understanding the scientific classification of the African penguin, we can appreciate its place in the broader context of penguin diversity and conservation.”
Conclusion
In conclusion, African penguins are a fascinating species found in the waters of South Africa. These beautiful creatures are known for the distinctive black band across their chests and the black spotting on their chest and belly.
Unfortunately, African penguins face numerous threats that have led to their vulnerable status. Factors such as food shortages, competition with commercial fisheries, human disturbance, weather events, and oil spills have contributed to the decline in their population.
However, there is hope for these incredible creatures. Conservation efforts and ongoing research play a vital role in protecting the habitat of African penguins and ensuring their survival for future generations.
Organizations like the International Bird Rescue Research Center are dedicated to responding to oil spills and helping affected penguins recover. It is crucial for us to address the factors that threaten their population, such as habitat destruction and overfishing of their primary food sources.
By learning more about African penguins, we can contribute to their conservation and appreciate the unique wonders of nature. Together, we can help raise awareness, support conservation efforts, and ensure that these amazing creatures continue to thrive in the waters of South Africa.
Let’s protect the African penguins and preserve the beauty of our natural world for generations to come.
FAQ
What is the African penguin’s scientific name?
The African penguin’s scientific name is Spheniscus demersus.
What is the size and weight of an African penguin?
African penguins are about 61 to 71 cm in size and can weigh up to 3.5 kg.
What do African penguins eat?
African penguins mainly eat anchovies and sardines, but they also consume squids, crustaceans, and other fishes.
How long is the incubation period for African penguins?
The incubation period for African penguins is about 38 days.
How many African penguins are there in the world?
The global population of African penguins is currently estimated to be around 180,000 individuals.
Why are African penguins considered vulnerable?
African penguins are considered vulnerable due to threats such as food shortages, competition with commercial fisheries, human disturbance, weather events, and oil spills.
What are the main threats to African penguins?
The main threats to African penguins include food shortages, competition with commercial fisheries, human disturbance, weather events, and oil spills.
How long do African penguins live?
African penguins have a lifespan of 15 to 20 years.
What organizations are involved in African penguin conservation?
Organizations like the International Bird Rescue Research Center are involved in African penguin conservation.
Do African penguins have any unique characteristics?
Yes, African penguins have bare patches on their faces and legs to dissipate heat. They also tend to nest throughout the year, unlike other penguin species.
Why is research important for African penguins?
Research helps scientists understand the behavior, ecology, and conservation needs of African penguins, which in turn informs conservation strategies and ensures their long-term survival.